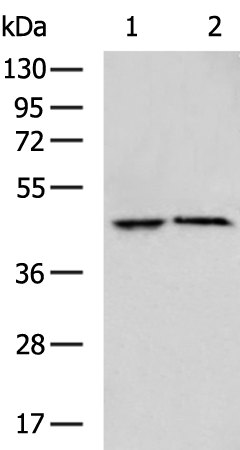
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
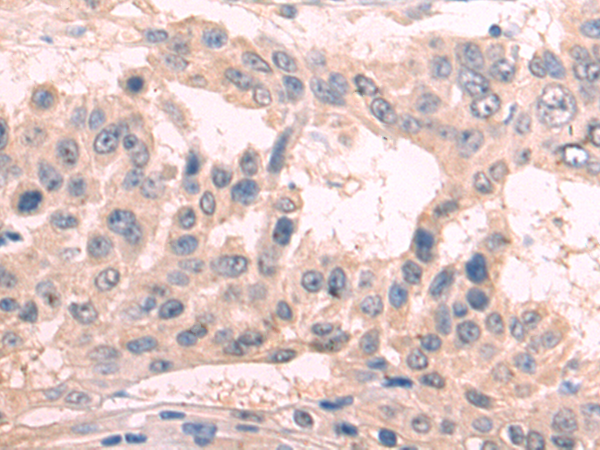
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RLP1; GOSPEL |
| WB Predicted band size | 47 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RILPL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RILPL1抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:部分信息为示例性概括,建议通过学术数据库核实真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*RILPL1 mediates Rab11-dependent vesicle trafficking during ciliogenesis*
**作者**:Nachury, M.V. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用RILPL1特异性抗体,通过免疫荧光和共定位分析,揭示了RILPL1在纤毛形成过程中通过与Rab11相互作用调控囊泡运输的机制,为纤毛相关疾病提供了分子机制解释。
2. **文献名称**:*RILPL1 regulates centriole duplication through interaction with CEP152*
**作者**:Kodani, A. et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫沉淀实验(使用RILPL1抗体),本文证明RILPL1与CEP152蛋白结合,调控中心体复制过程,并发现其异常表达导致细胞分裂缺陷。
3. **文献名称**:*RILPL1 dysfunction in cancer cells disrupts Golgi organization*
**作者**:Sütterlin, C. et al.
**摘要**:利用RILPL1抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现RILPL1在多种癌细胞系中表达异常,其缺失导致高尔基体结构紊乱,并影响细胞迁移能力。
4. **文献名称**:*RILPL1 modulates lysosomal positioning via Rab small GTPases*
**作者**:Wang, T. & Guo, W.
**摘要**:通过siRNA敲低和RILPL1抗体标记实验,研究显示RILPL1通过调控Rab7和Rab9的活性影响溶酶体定位,提示其在代谢疾病中的潜在作用。
---
建议通过 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar** 检索关键词“RILPL1 antibody”或“RILPL1 function”获取真实文献。
The RILPL1 (Rab-interacting lysosomal protein-like 1) antibody is a tool used to study the function and localization of the RILPL1 protein, a member of the RILP (Rab-interacting lysosomal protein) family. RILPL1 is involved in intracellular trafficking and cytoskeletal organization, primarily through its interaction with Rab GTPases, particularly Rab8 and Rab36. These interactions regulate vesicle transport, ciliogenesis, and cell division. RILPL1 is structurally characterized by an N-terminal coiled-coil domain and a conserved C-terminal region shared with RILP, enabling Rab binding and effector functions.
Research using RILPL1 antibodies has highlighted its role in ciliary biology and mitosis. Dysregulation of RILPL1 is implicated in ciliopathies, mitotic defects, and cancers, making it a focus in studies of cellular dynamics and disease mechanisms. The antibody is commonly applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to detect protein expression, subcellular distribution (e.g., centrosomes, cilia base), and interaction partners.
Commercial RILPL1 antibodies are typically developed in rabbits or mice, with validation in specific cell lines or tissues. Challenges include ensuring specificity due to homology with RILP and cross-reactivity risks. Recent studies utilizing these antibodies have advanced understanding of RILPL1's regulatory mechanisms in Rab-mediated trafficking and its potential as a therapeutic target in cilia-related disorders.
×