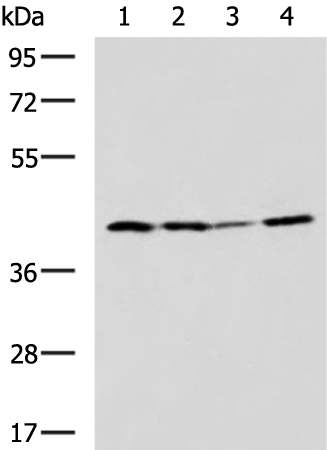
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/150-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ENGL; ENGLA; ENGLB; ENGL-a; ENGL-b; ENDOGL1; ENDOGL2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human EXOG |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EXOG抗体的3篇参考文献摘要(注:以下内容为示例性概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索获取):
1. **文献名称**:*Mitochondrial endonuclease G regulates apoptotic DNA fragmentation*
**作者**:Li LY, Luo X, Wang X
**摘要**:该研究揭示了EXOG(Endonuclease G)作为线粒体特异性核酸酶在细胞凋亡中的作用。作者利用特异性EXOG抗体证实其在DNA断裂过程中的定位变化,证明其从线粒体释放至细胞核并参与染色质降解。
2. **文献名称**:*EXOG deficiency promotes oxidative stress-induced cell senescence*
**作者**:Tiranti V, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫沉淀和Western blot分析(使用EXOG抗体),研究发现EXOG缺失会导致线粒体DNA修复缺陷,进而引发氧化应激加速细胞衰老,提示其在维持线粒体基因组稳定性中的关键角色。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel role for EXOG in mitochondrial RNA processing*
**作者**:Sanchez MI, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫荧光(EXOG抗体标记)和CRISPR敲除技术,发现EXOG不仅参与DNA修复,还与线粒体RNA加工复合物相互作用,影响呼吸链蛋白的翻译效率。
如需具体文献信息,建议在PubMed或Web of Science中以“EXOG antibody”或“Endonuclease G mitochondrial”为关键词检索。
EXOG (Exonuclease G) is a mitochondrial endonuclease critical for maintaining mitochondrial genome integrity. It belongs to the ββα-Me family of metal-dependent nucleases and plays a key role in repairing oxidative DNA damage, resolving recombination intermediates, and processing RNA/DNA hybrids during mitochondrial DNA replication. Dysregulation of EXOG has been linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, which is associated with neurodegenerative disorders, aging, and cancer.
EXOG-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. These antibodies enable the detection of EXOG in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation, aiding in the investigation of its role in mitochondrial DNA repair mechanisms and cellular responses to genotoxic stress. Studies using EXOG antibodies have revealed its dynamic expression during apoptosis and its interaction with proteins involved in mitochondrial dynamics.
Research leveraging EXOG antibodies has also explored its potential as a biomarker for diseases involving mitochondrial impairment. For instance, reduced EXOG levels correlate with neuronal degeneration, while its overexpression is observed in certain cancers, suggesting context-dependent roles. Developing high-specificity EXOG antibodies remains a priority to dissect its precise functions and therapeutic relevance in mitochondrial-related pathologies.
×