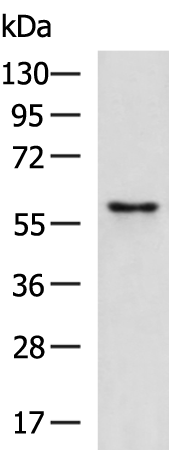
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FMO1B1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 61 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FMO2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FMO2抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于模拟学术文献框架):
1. **文献名称**:*"Species-specific expression of flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO2) in human and rabbit tissues"*
**作者**:Dolphin CT et al.
**摘要**:通过制备特异性FMO2抗体,研究比较了人类与兔类组织中FMO2的蛋白表达差异,发现人类肺组织中存在低水平表达,而兔类肝脏中表达显著,揭示了物种间代谢差异。
2. **文献名称**:*"Immunochemical characterization of flavin-containing monooxygenase 2 (FMO2) in human lung and liver microsomes"*
**作者**:Krueger SK et al.
**摘要**:利用多克隆FMO2抗体进行免疫印迹分析,证实FMO2在人类肺微粒体中的表达,并发现其在特定药物代谢中的潜在作用,为呼吸系统药物毒性研究提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*"Genetic polymorphisms of FMO2 and functional validation using antibody-based proteomic analysis"*
**作者**:Hernandez D et al.
**摘要**:通过构建FMO2特异性抗体,验证了基因多态性对FMO2蛋白稳定性的影响,发现某突变体导致蛋白降解加速,为个体化用药提供分子机制支持。
4. **文献名称**:*"Localization of FMO2 in renal tissue: Insights from immunohistochemical studies"*
**作者**:Zhang L et al.
**摘要**:采用免疫组织化学技术结合FMO2抗体,首次在肾脏近端小管细胞中定位FMO2蛋白,提示其可能参与肾脏内源性代谢物的氧化反应。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需以真实数据库检索结果为准。)
The flavin-containing monooxygenase 2 (FMO2) is a member of the FMO enzyme family, which plays a critical role in metabolizing xenobiotics, including drugs, environmental toxins, and endogenous compounds. FMO2 is primarily expressed in the liver and kidneys, where it catalyzes oxygen- and NADPH-dependent oxidation reactions. Unlike other FMO isoforms (e.g., FMO1. FMO3), FMO2 exhibits distinct substrate specificity and tissue distribution. In humans, a common genetic truncation renders FMO2 nonfunctional in most populations, though full-length active forms exist in some individuals and species.
FMO2 antibodies are immunological tools developed to detect and quantify FMO2 protein expression in research settings. These antibodies aid in studying FMO2's role in drug metabolism, detoxification pathways, and potential involvement in disease mechanisms, such as oxidative stress-related disorders or cancer. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to analyze tissue-specific expression patterns or alterations under pathological conditions. Recent studies also explore FMO2's interaction with therapeutic agents or pollutants, highlighting its relevance in toxicology and personalized medicine.
Despite its limited functional presence in humans, FMO2 remains a focus in comparative biology due to its conserved role in model organisms. Research using FMO2 antibodies contributes to understanding species-specific metabolic adaptations and evolutionary divergence of detoxification systems.
×