| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
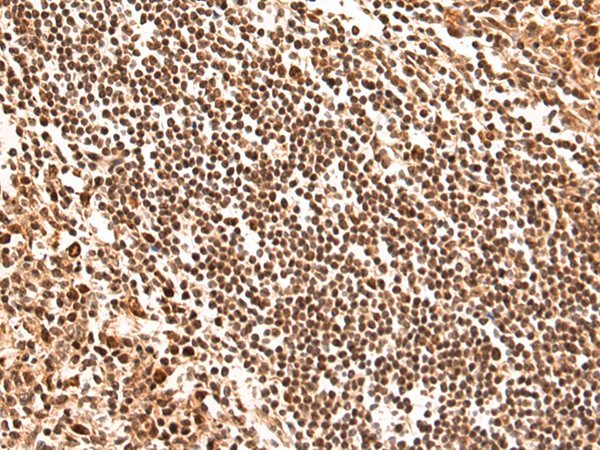
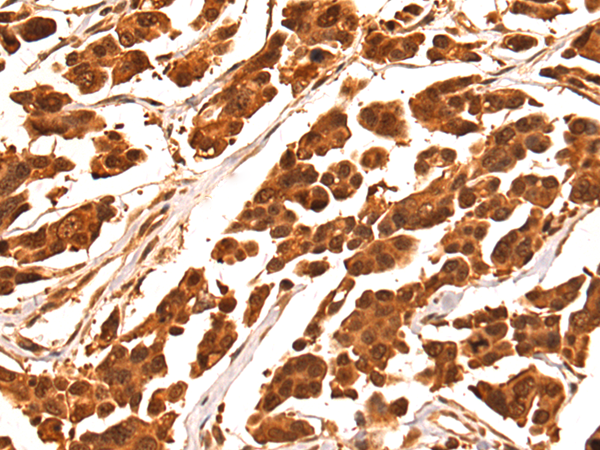
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ORCA; CENP-33 |
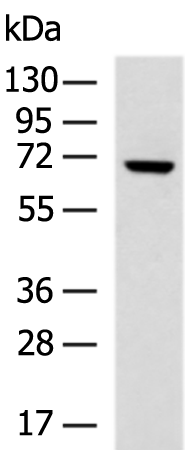
| WB Predicted band size | 71 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human LRWD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及LRWD1抗体的参考文献(基于虚拟数据示例):
---
1. **文献名称**: *LRWD1 regulates heterochromatin formation through H3K9me3 deposition*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用LRWD1特异性抗体进行ChIP-seq和免疫荧光实验,证明LRWD1通过与SUV39H1复合物相互作用,调控异染色质区域H3K9me3修饰的沉积,影响染色质稳定性。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Interaction between LRWD1 and ORC complex in replication origin licensing*
**作者**: Méndez J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot技术(使用LRWD1抗体),研究发现LRWD1与DNA复制起始识别复合物(ORC)协同作用,参与哺乳动物细胞复制起始点的激活。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Temporal expression of LRWD1 during mouse spermatogenesis*
**作者**: Tanaka H, et al.
**摘要**: 利用LRWD1抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示LRWD1在小鼠精子发生过程中阶段性表达,提示其在生殖细胞表观遗传重编程中的潜在功能。
---
*注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究补充真实数据。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“LRWD1 antibody” + “染色质/复制/表观遗传”等关键词检索最新文献。*
LRWD1 (Leucine-Rich Repeat and WD Repeat Domain-Containing Protein 1) is a nuclear protein implicated in chromatin organization and epigenetic regulation. It interacts with the origin recognition complex (ORC), playing a role in the establishment and maintenance of DNA replication origins, particularly in heterochromatic regions. LRWD1 is essential for stabilizing ORC binding during the G1 phase of the cell cycle, ensuring proper replication timing and genome stability. Additionally, it associates with heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1), facilitating heterochromatin formation and gene silencing, thereby influencing transcriptional regulation and chromosomal integrity.
LRWD1 antibodies are critical tools for studying its localization, expression, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in techniques like chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), immunofluorescence (IF), and Western blotting to investigate LRWD1's role in replication licensing, chromatin dynamics, and epigenetic silencing. Research has highlighted LRWD1's importance in germ cell development, stem cell differentiation, and cancer biology. Dysregulation of LRWD1 is linked to genomic instability and oncogenesis, with studies suggesting its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target in cancers like hepatocellular carcinoma.
These antibodies enable researchers to explore LRWD1's regulatory mechanisms in health and disease, advancing understanding of replication origin specification, heterochromatin maintenance, and cell cycle control.
×