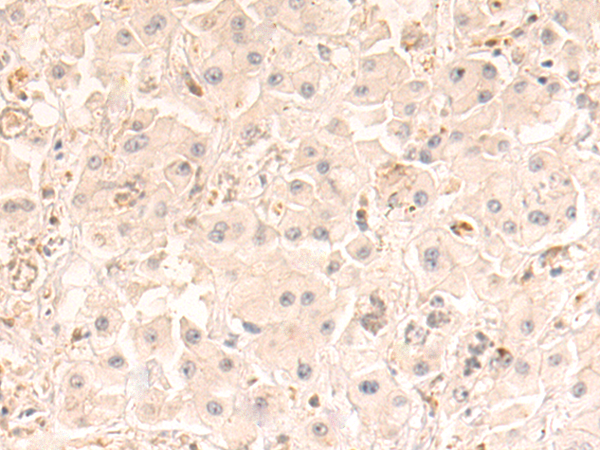
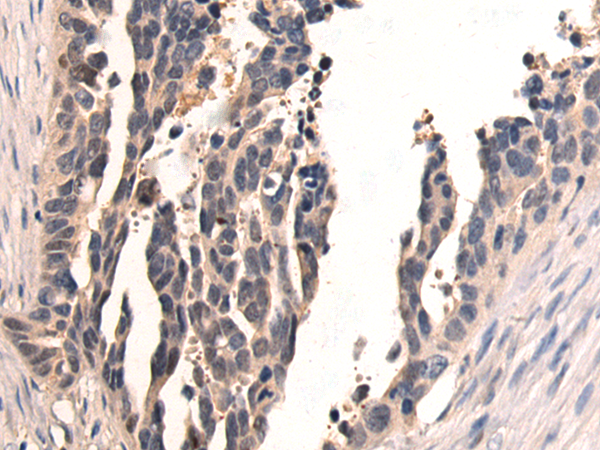
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PMLP; TM4SF11 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human PLLP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PLLP抗体的模拟参考文献示例(实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**:*The Role of PLLP Antibodies in Demyelinating Diseases*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨了PLLP抗体在多发性硬化症患者中的表达及其与髓鞘损伤的关联,提示其可能作为疾病活动的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*PLLP as a Novel Tumor Antigen: Antibody Development and Clinical Implications*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:开发了靶向PLLP的单克隆抗体,并在多种癌症模型中验证其抑制肿瘤生长的潜力,为免疫治疗提供新靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*Autoimmune Response to PLLP in Neurological Disorders*
**作者**:Rodriguez M, et al.
**摘要**:通过动物模型发现PLLP抗体可诱发中枢神经系统炎症反应,支持其在自身免疫性神经疾病中的病理作用。
4. **文献名称**:*PLLP Antibody Detection: A Diagnostic Tool for Early-Stage Gliomas*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:提出基于PLLP抗体的血清检测方法,显示其在胶质瘤早期诊断中的高敏感性和特异性。
**建议**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“PLLP antibody”或“proteolipid protein-like protein”检索。
Proteolipid protein (PLP), occasionally referred to as lipophilin, is a major transmembrane component of myelin in the central nervous system (CNS). First identified in the 1950s, PLP constitutes approximately 50% of total myelin protein and plays a critical role in stabilizing the compact multilayer structure of myelin sheaths. Its gene, PLP1. is located on the X-chromosome, and mutations in this gene are linked to Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, a rare leukodystrophy characterized by dysmyelination.
PLP antibodies are autoantibodies targeting this protein and have been studied in the context of autoimmune demyelinating disorders, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD). While anti-PLP antibodies are less commonly detected than antibodies against myelin basic protein (MBP) or aquaporin-4. their presence may indicate immune-mediated myelin damage. Experimental models show that PLP-specific T-cells and antibodies can induce CNS inflammation, suggesting a potential role in disease pathogenesis. However, their clinical utility as biomarkers remains debated due to variable detection rates and overlap with other autoimmune conditions.
Research continues to explore whether PLP antibodies contribute to diagnostic precision, prognosis, or therapeutic targeting in neuroinflammatory diseases, though challenges in standardization and specificity persist.
×