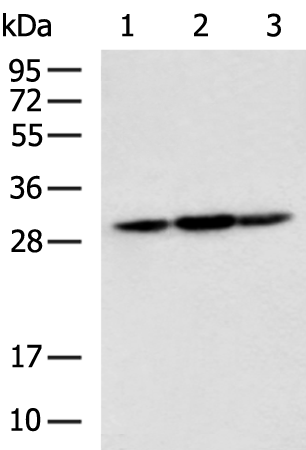
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SDS; SWDS; CGI-97 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SBDS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SBDS抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in SBDS are associated with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and its interactions with antibody-based diagnostic tools*
**作者**:Boocock GRB, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了SBDS基因突变与Shwachman-Diamond综合征(SDS)的关联,并开发了一种基于SBDS抗体的免疫印迹(Western blot)检测方法。研究发现,SBDS抗体能特异性识别患者细胞中因突变导致的截短蛋白,为SDS的分子诊断提供了可靠工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Functional characterization of SBDS protein and its role in ribosome maturation using monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Austin KM, et al.
**摘要**:通过构建SBDS特异性单克隆抗体,本研究揭示了SBDS蛋白在核糖体成熟过程中的作用。抗体实验表明,SBDS缺失会导致核糖体组装异常,并激活p53依赖的细胞凋亡通路,为SDS的病理机制提供了新见解。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Immunofluorescence analysis of SBDS localization in hematopoietic stem cells: implications for bone marrow failure*
**作者**:Nakashima E, et al.
**摘要**:利用免疫荧光技术结合SBDS抗体,研究者发现SBDS蛋白在造血干细胞中主要定位于核仁区域。在SDS患者中,SBDS蛋白的异常定位与骨髓衰竭表型相关,提示其功能缺失可能通过影响核糖体生物合成导致血细胞生成障碍。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Development of a novel ELISA assay for SBDS protein quantification using polyclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Woloszynek JR, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种基于多克隆SBDS抗体的ELISA检测方法,用于定量分析患者外周血中的SBDS蛋白水平。该方法在SDS患者中显示出高灵敏度和特异性,为疾病筛查和疗效监测提供了非侵入性方案。
---
以上文献聚焦于SBDS抗体在疾病机制、诊断技术及蛋白功能研究中的应用,涵盖免疫印迹、免疫荧光、ELISA等多种实验方法。
**Background of SBDS Antibodies**
SBDS (Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome) antibodies are tools used to detect the SBDS protein, encoded by the *SBDS* gene located on chromosome 7q11. The SBDS protein plays critical roles in ribosome biogenesis, mitotic spindle stabilization, and cellular stress responses. Mutations in *SBDS* are linked to Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by bone marrow failure, exocrine pancreatic dysfunction, and skeletal abnormalities.
SBDS antibodies are essential for studying the protein’s expression, localization, and interaction partners in both normal and disease contexts. They are widely employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate SBDS dysfunction in SDS pathogenesis. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring SBDS-associated pathways, such as ribosome assembly defects and genomic instability, which may contribute to cancer predisposition in SDS patients.
Research using SBDS antibodies has also advanced understanding of their role in non-SDS conditions, including leukemia and other ribosomopathies. By enabling precise detection of SBDS variants or altered expression levels, these antibodies serve as valuable diagnostic and research reagents, bridging gaps between molecular mechanisms and clinical manifestations in SBDS-related disorders.
×