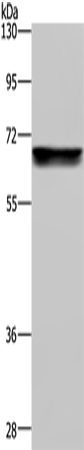
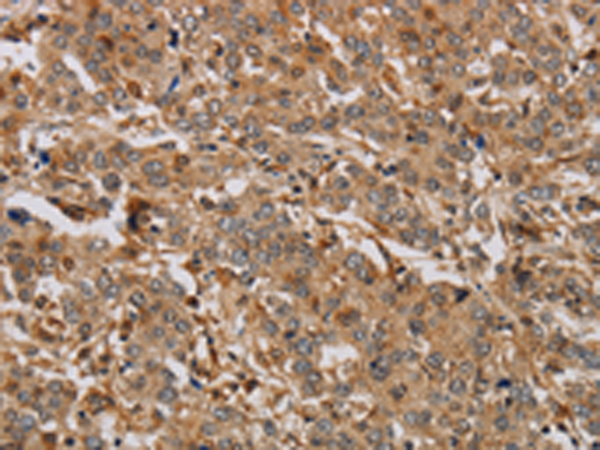
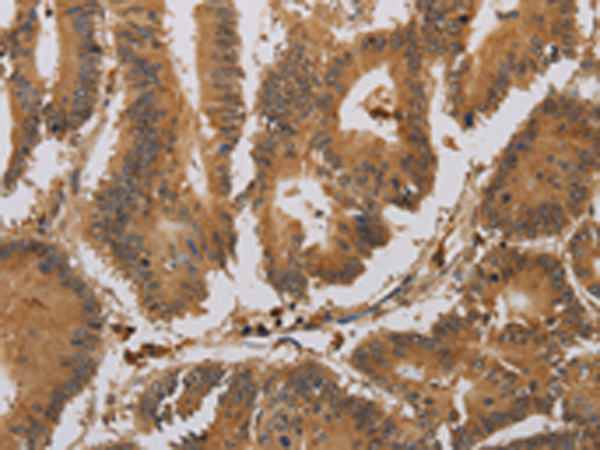
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | YT; ACEE; ARACHE; N-ACHE |
| WB Predicted band size | 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ACHE |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ACHE抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括,供参考:
---
1. **《Autoantibodies to acetylcholinesterase in paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration》**
作者:Carrie M. Ellezam et al.
摘要:研究报道了在副肿瘤性小脑变性(PCD)患者血清中发现特异性抗乙酰胆碱酯酶(ACHE)自身抗体,提示ACHE可能作为神经系统副肿瘤综合征的潜在抗原靶点,抗体水平与疾病进展相关。
---
2. **《Acetylcholinesterase antibodies in Sjögren's syndrome》**
作者:L. S. K. Walker et al.
摘要:该文献分析了干燥综合征(Sjögren's syndrome)患者中ACHE抗体的检出率及其与自主神经功能障碍的关联,发现抗体可能通过干扰胆碱能信号传导导致腺体分泌异常。
---
3. **《Anti-acetylcholinesterase antibodies as a biomarker for colorectal cancer detection》**
作者:H. Li et al.
摘要:研究提出血清中ACHE抗体在结直肠癌患者中的表达显著升高,可能通过抑制酶活性促进肿瘤微环境炎症反应,或可作为新型癌症诊断生物标志物。
---
如需具体文献全文或更多信息,可通过PubMed或Sci-Hub输入标题检索。
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) antibodies are immunological tools designed to target the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which plays a critical role in terminating synaptic transmission at cholinergic junctions. AChE catalyzes the hydrolysis of acetylcholine (ACh), a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle activation and cognitive functions, into choline and acetate. This enzymatic activity ensures precise control of nerve impulse transmission, preventing excessive stimulation. Dysregulation of AChE is implicated in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, where reduced ACh levels correlate with cognitive decline, and in myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disorder affecting neuromuscular signaling.
AChE antibodies are widely utilized in research and diagnostics. In neuroscience, they help localize AChE expression in tissues, study its role in synaptic plasticity, and investigate its interaction with toxins (e.g., organophosphates) or therapeutic agents (e.g., donepezil). Clinically, these antibodies assist in diagnosing autoimmune conditions or monitoring pesticide exposure. Recent studies also explore AChE's non-classical roles in cell differentiation and apoptosis, expanding its relevance in cancer and inflammation research.
However, challenges persist, including cross-reactivity with butyrylcholinesterase, a structurally similar enzyme. Advances in monoclonal antibody technology aim to improve specificity, enhancing their utility in targeted therapies and biomarker discovery. Overall, AChE antibodies remain pivotal in bridging molecular mechanisms of cholinergic signaling with translational applications.
×