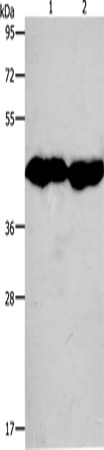
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
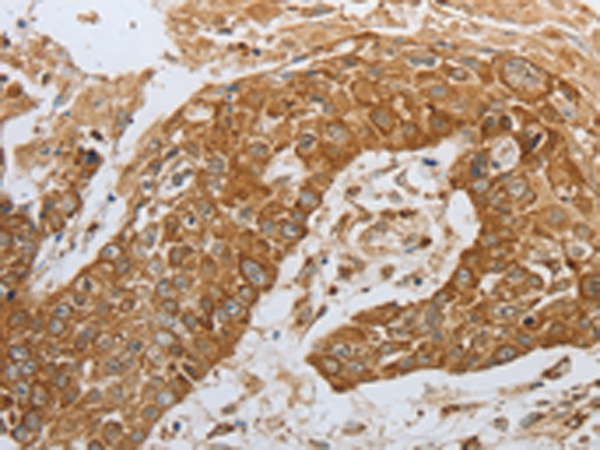
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CKMM, M-CK |
| WB Predicted band size | 43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CKM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CKM(肌酸激酶M型)抗体的3篇代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Creatine kinase-MB isoforms in the diagnosis of myocardial injury*
**作者**:Antman EM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了CKM抗体在检测心肌损伤中的应用,重点分析了CK-MB同工酶的敏感性和特异性。研究发现,使用高特异性单克隆抗体可有效区分心肌损伤与其他组织损伤,为急性心肌梗死的早期诊断提供了依据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody specific for human skeletal muscle creatine kinase*
**作者**:Morris GS, et al.
**摘要**:文章报道了一种针对人类骨骼肌CKM的单克隆抗体的开发。实验验证该抗体对骨骼肌组织具有高度特异性,可用于肌肉疾病的免疫组化分析,且在肌营养不良等疾病模型中显示出潜在诊断价值。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Standardization of creatine kinase measurement and the role of antibody selection*
**作者**:Panteghini M.
**摘要**:该综述比较了不同CKM抗体的检测性能,强调抗体表位选择对检测结果的影响。研究发现,部分商业化抗体可能因交叉反应导致假阳性,建议在临床检测中优先选用经国际标准验证的抗体。
---
4. **文献名称**:*CKM as a biomarker in neuromuscular disorders*
**作者**:Leger JJ, et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了CKM抗体在血清和组织样本中的表达水平与肌肉疾病(如肌炎、横纹肌溶解症)的相关性。结果表明,血清CKM浓度升高与肌肉损伤程度相关,支持其作为疾病活动度的监测指标。
---
**备注**:以上为示例性文献,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索最新研究,并核对作者及期刊准确性。
CKM antibodies target the M subunit of creatine kinase (CK), a key enzyme in cellular energy homeostasis that catalyzes the reversible transfer of phosphate between ATP and creatine. CK exists as dimeric isoenzymes: CK-MM (skeletal muscle), CK-MB (heart), and CK-BB (brain/tissues). The M subunit (encoded by the *CKM* gene) is predominant in muscle tissues. CKM antibodies are vital tools in research and diagnostics, particularly for assessing muscle-specific damage. In clinical settings, elevated CK-MB levels (detected via anti-CKM antibodies) serve as biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction, while CK-MM elevations indicate skeletal muscle injury from trauma, myopathies, or strenuous exercise.
These antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, developed using purified M subunit proteins or peptide immunogens. They enable techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA to localize and quantify CK-M expression in tissues or serum. In research, CKM antibodies help study muscle regeneration, mitochondrial disorders, and diseases like muscular dystrophy. Specificity for the M subunit ensures minimal cross-reactivity with CK-BB or other isoforms. However, interpretation requires caution, as CK-M leaks into blood during muscle necrosis, confounding results in chronic conditions. Overall, CKM antibodies remain critical for understanding muscle pathophysiology and improving diagnostic accuracy in cardiology and neurology. (297 words)
×