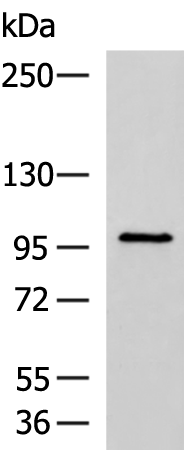
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KD; AIS; AR8; TFM; DHTR; SBMA; HYSP1; NR3C4; SMAX1; HUMARA |
| WB Predicted band size | 99 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human AR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于AR(雄激素受体)抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要总结其核心内容:
1. **《Tissue-specific expression of the human prostate-specific antigen gene in transgenic mice: roles of androgen and its receptor》**
- **作者**: Cleutjens KB et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究利用转基因小鼠模型,揭示了雄激素受体(AR)在前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)基因表达中的调控作用,并通过AR抗体检测证实了AR与DNA结合的功能区域,为AR在靶基因调控中的机制提供了实验依据。
2. **《Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression》**
- **作者**: Heinlein CA & Chang C
- **摘要**: 综述了AR信号通路在前列腺癌发生和耐药性中的作用,强调了AR抗体在检测受体表达水平、亚细胞定位及磷酸化状态中的应用,以评估癌症进展和治疗反应。
3. **《Resistance to CYP17A1 inhibition with abiraterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer: induction of steroidogenesis and androgen receptor splice variants》**
- **作者**: Li Y et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过AR抗体(如针对AR全长和AR-V7变体的特异性抗体)发现,去势抵抗性前列腺癌中AR剪接变体的表达上调与药物抵抗相关,为靶向AR不同亚型的抗体开发提供了方向。
这些文献分别从AR的功能机制、病理作用及治疗抵抗角度,展示了AR抗体在基础研究与临床诊断中的应用价值。
Androgen receptor (AR) antibodies are critical tools in studying the role of the androgen receptor, a nuclear receptor superfamily protein that mediates the effects of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. The AR is essential for male sexual development, prostate function, and maintaining secondary sexual characteristics. Dysregulation of AR signaling is implicated in pathologies such as prostate cancer, androgen insensitivity syndrome, and polycystic ovary syndrome. AR antibodies enable researchers to detect, quantify, and localize AR expression in tissues or cells, providing insights into its biological and pathological roles.
In research, AR antibodies are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study AR expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interactions with co-regulators. Clinically, they aid in diagnosing AR-related disorders and assessing prostate cancer progression. For instance, elevated AR levels or mutations detected via these antibodies may correlate with resistance to androgen-deprivation therapies. Additionally, AR splice variants (e.g., AR-V7), identified using variant-specific antibodies, are biomarkers for predicting treatment response in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
The development of AR-targeted therapies, such as AR antagonists (e.g., enzalutamide) and degraders, has further driven the need for reliable AR antibodies to evaluate drug efficacy and mechanism. Moreover, studies on post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) of AR, detectable through modification-specific antibodies, help unravel regulatory mechanisms influencing AR activity. As precision oncology advances, AR antibodies remain pivotal in stratifying patients for tailored therapies and advancing understanding of androgen-driven diseases.
×