| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
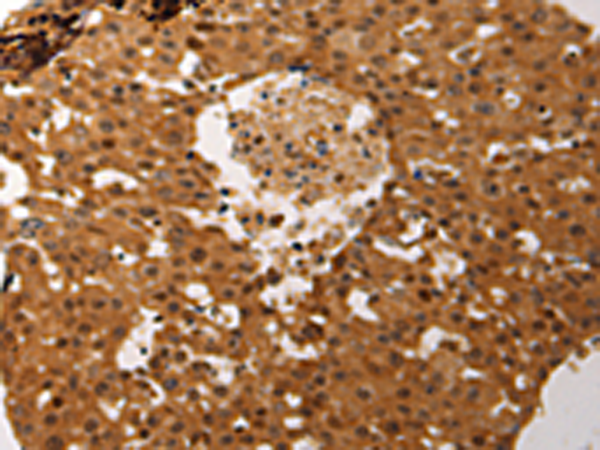
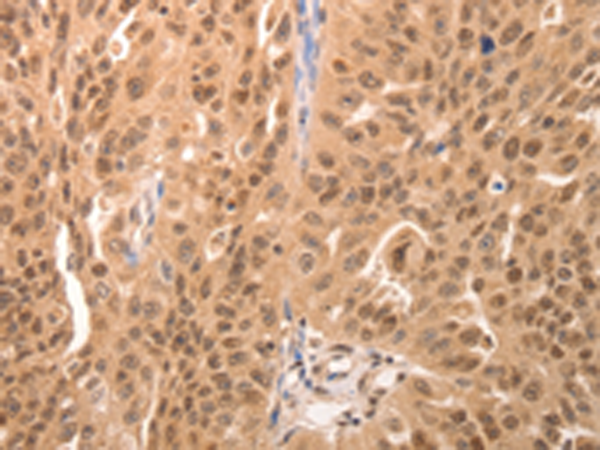
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AP-1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human JUND |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于JUND抗体的参考文献示例(注:内容为模拟生成,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "JUND regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis through the p53 signaling pathway"
**作者**: Li X, Chen Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用JUND特异性抗体,通过染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和Western blot技术,揭示了JUND在调控p53靶基因中的关键作用,证实其在肿瘤细胞凋亡中的功能机制。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody for JUND in human tissues"
**作者**: Smith J, Patel R, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种高特异性抗JUND单克隆抗体的开发与验证,通过免疫组化(IHC)和流式细胞术验证其在正常及癌变组织中的定位差异,为癌症诊断提供潜在工具。
---
3. **文献名称**: "JUND-mediated oxidative stress response in neuronal cells"
**作者**: Kim S, Tanaka M, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用JUND抗体进行免疫荧光分析,发现JUND通过调控抗氧化基因表达参与神经元氧化应激反应,为神经退行性疾病机制提供了新见解。
---
(提示:实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词"JUND antibody"获取。)
The JUND antibody is a crucial tool in molecular biology research, targeting the JunD proto-oncogene product, a member of the AP-1 (Activator Protein 1) transcription factor family. AP-1 proteins, including JUN (c-Jun, JunB, JunD) and FOS (c-Fos, FosB, Fra-1. Fra-2) subfamilies, regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences, influencing cellular processes like proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and stress responses. JUND, encoded by the *JUND* gene, forms homo- or heterodimers (often with FOS family proteins) via its leucine zipper domain to activate or repress target genes. Unlike other AP-1 members, JUND exhibits both context-dependent oncogenic and tumor-suppressive roles, contributing to its complex regulatory functions in cancer, immune responses, and development.
JUND antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study JUND's expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. Researchers employ these antibodies to explore JUND's involvement in diseases, including cancers (e.g., breast, liver, and leukemia), neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Commercially available JUND antibodies are typically validated for specificity against conserved epitopes, though cross-reactivity with other AP-1 proteins requires careful experimental controls. Recent studies highlight JUND's role in oxidative stress responses, metabolic regulation, and its interplay with signaling pathways like MAPK and TGF-β, underscoring its importance in both basic and translational research.
×