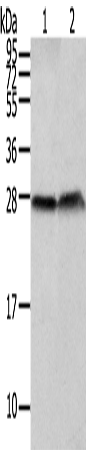
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
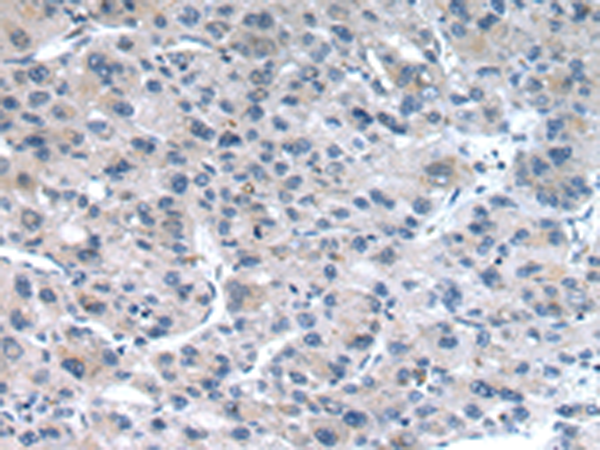
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HOMG5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CLDN19 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CLDN19抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟内容,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**: "CLDN19 mutations cause familial hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis through impaired tight junction integrity"
**作者**: Konrad M. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示了CLDN19基因突变通过破坏肾小管上皮细胞紧密连接,导致镁离子重吸收障碍,进而引发家族性低镁血症。研究利用CLDN19特异性抗体进行免疫组化分析,证实突变蛋白在细胞膜上的异常定位。
2. **文献名称**: "CLDN19 as a potential biomarker in gastric cancer: Expression analysis using a novel monoclonal antibody"
**作者**: Li Y. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种高特异性抗CLDN19单克隆抗体,用于检测胃癌组织中CLDN19的异常表达。结果显示,CLDN19在肿瘤组织中的表达下调与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能作为胃癌诊断的标志物。
3. **文献名称**: "Targeting CLDN19 in metastatic breast cancer: A therapeutic antibody approach"
**作者**: Smith J.R. et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种靶向CLDN19的人源化单抗,并在乳腺癌转移模型中验证其疗效。实验表明,该抗体通过阻断CLDN19介导的细胞间黏附,抑制肿瘤细胞侵袭和转移,为CLDN19高表达肿瘤提供了潜在治疗策略。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索真实发表的论文。)
Claudin-19 (CLDN19) is a member of the claudin family, transmembrane proteins critical for forming tight junctions that regulate paracellular permeability and maintain cell polarity. CLDN19 is particularly abundant in the kidney and retina. In the kidney, it co-expresses with CLDN16 in the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop, forming a selective paracellular barrier for magnesium and calcium reabsorption. Mutations in *CLDN19* are linked to familial hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis (FHHNC), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by renal magnesium wasting, kidney stones, and progressive renal failure. In the retina, CLDN19 contributes to the blood-retinal barrier, and its dysfunction may underlie ocular abnormalities observed in some FHHNC patients.
CLDN19-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its localization, expression, and functional roles in health and disease. They enable detection of CLDN19 in tissue samples via immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, or immunofluorescence, aiding in diagnosing CLDN19-related pathologies or validating experimental models. Research using these antibodies has clarified how CLDN19 interacts with other claudins (e.g., CLDN16) and how mutations disrupt tight junction integrity. Therapeutic applications, such as antibody-based targeting to modulate tight junction function, remain exploratory but hold potential for treating electrolyte disorders or barrier-related diseases. Overall, CLDN19 antibodies are pivotal in advancing understanding of epithelial barrier biology and translational research.
×