| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
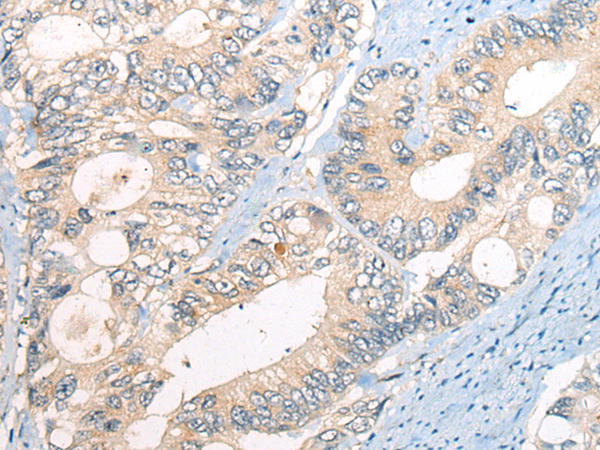
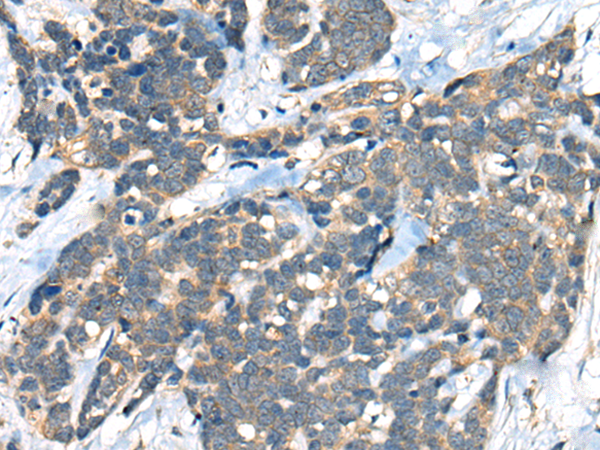
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD; GSE; GRD4; ALPS5; CD152; CTLA-4; IDDM12; CELIAC3 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CTLA4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CTLA4抗体的经典文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma*
**作者**:Hodi FS, et al.
**摘要**:该III期临床试验首次证明抗CTLA4抗体Ipilimumab可显著延长晚期黑色素瘤患者的总生存期(OS),奠定了CTLA4免疫检查点阻断在肿瘤治疗中的里程碑地位。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Enhancement of Antitumor Immunity by CTLA-4 Blockade*
**作者**:Leach DR, Krummel MF, Allison JP
**摘要**:此基础研究阐明了CTLA4抗体通过解除T细胞抑制信号、增强抗肿瘤免疫应答的机制,为后续临床转化提供了理论依据(发表于1996年《Science》)。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Nivolumab and Ipilimumab versus Ipilimumab in Untreated Melanoma*
**作者**:Wolchok JD, et al.
**摘要**:研究显示,CTLA4抗体Ipilimumab联合PD-1抗体Nivolumab治疗晚期黑色素瘤,较单药显著提高客观缓解率(ORR)和无进展生存期(PFS),确立联合免疫治疗新策略。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Five-Year Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma*
**作者**:Larkin J, et al.
**摘要**:长期随访数据证实,CTLA4与PD-1双免疫检查点抑制剂联用可使晚期黑色素瘤患者5年生存率达52%,但需注意治疗相关不良反应的管理。
---
以上文献涵盖关键临床试验、机制研究及长期疗效验证,反映了CTLA4抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的核心地位。
CTLA4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4), a critical immune checkpoint protein, was first identified in the 1980s as a homolog of CD28. It is primarily expressed on regulatory T cells (Tregs) and activated T cells, functioning as a negative regulator of T-cell activation. Unlike CD28. which provides co-stimulatory signals upon binding to B7 molecules (CD80/CD86) on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), CTLA4 exhibits higher affinity for B7 ligands, competitively inhibiting CD28-B7 interactions and suppressing early T-cell activation in lymphoid organs. This mechanism prevents excessive immune responses and maintains self-tolerance.
In the mid-1990s, James Allison’s groundbreaking work demonstrated that blocking CTLA4 with antibodies enhanced antitumor immunity in preclinical models. This led to the development of ipilimumab, the first FDA-approved CTLA4 inhibitor (2011), for metastatic melanoma. By disrupting CTLA4-mediated inhibitory signals, these antibodies promote T-cell proliferation and tumor infiltration, though often triggering immune-related adverse events due to widespread immune activation. Despite modest response rates as monotherapy, CTLA4 inhibitors laid the foundation for cancer immunotherapy, particularly in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 blockers, improving outcomes in multiple cancers. Research continues to optimize dosing, minimize toxicity, and identify predictive biomarkers to refine clinical applications.
×