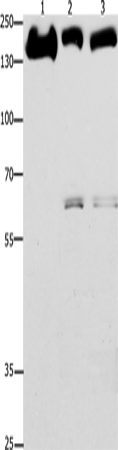
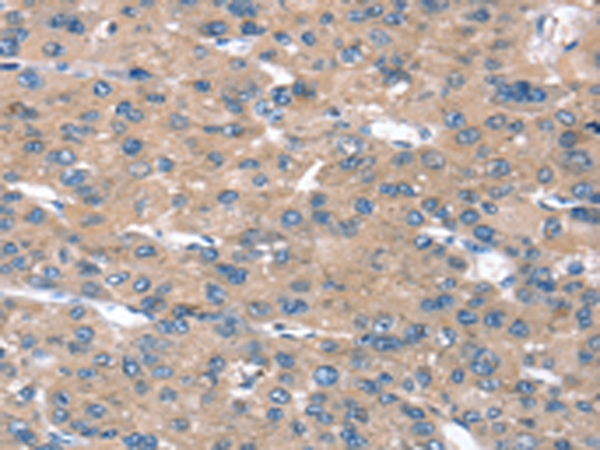
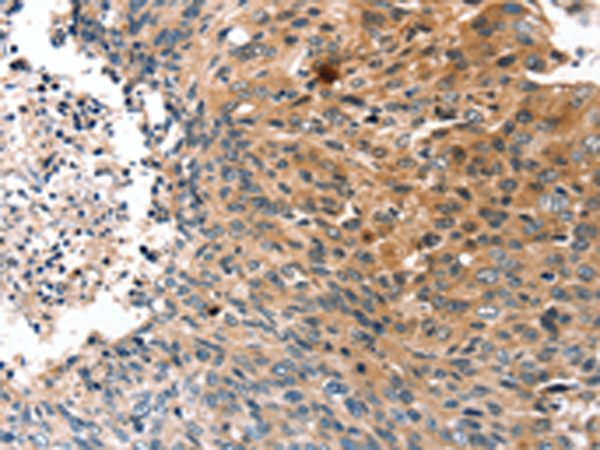
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ERBB, HER1, mENA, ERBB1, PIG61 |
| WB Predicted band size | 134 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human EGFR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EGFR抗体的3-4篇代表性文献的简要总结:
1. **文献名称**:Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer
**作者**:Van Cutsem, E. et al.
**摘要**:该研究(CRYSTAL试验)表明,西妥昔单抗(EGFR单克隆抗体)联合标准化疗(FOLFIRI)可显著延长KRAS野生型转移性结直肠癌患者的无进展生存期,确立了EGFR靶向治疗在此类患者中的临床价值。
2. **文献名称**:Panitumumab versus cetuximab in patients with chemotherapy-refractory wild-type KRAS exon 2 metastatic colorectal cancer
**作者**:Heinemann, V. et al.
**摘要**:比较帕尼单抗(全人源化EGFR抗体)与西妥昔单抗(人鼠嵌合抗体)在KRAS野生型结直肠癌中的疗效,结果显示两者总生存期相似,但帕尼单抗的免疫原性更低,安全性更优。
3. **文献名称**:EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy
**作者**:Lynch, T.J. et al.
**摘要**:发现非小细胞肺癌患者中EGFR基因突变(如外显子19缺失)与EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(如吉非替尼)的敏感性相关,为EGFR靶向治疗的精准用药提供了分子标志物依据。
4. **文献名称**:Resistance to EGFR blockade in colorectal cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
**作者**:Wheeler, D.L. et al.
**摘要**:综述了EGFR抗体治疗结直肠癌的耐药机制,包括KRAS/BRAF突变、EGFR胞外域变异及旁路信号激活,并提出联合靶向治疗或可逆转耐药。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对具体出版信息及原文内容。)
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor involved in regulating cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Overexpression or mutations in EGFR are frequently linked to cancer progression, notably in non-small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and glioblastoma. This makes EGFR a critical therapeutic target.
EGFR monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), such as cetuximab and panitumumab, bind to the extracellular domain of EGFR, blocking ligand-induced activation and downstream signaling pathways like RAS-RAF-MAPK and PI3K-AKT. By inhibiting these pathways, EGFR antibodies suppress tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. They are clinically approved for cancers with wild-type EGFR or specific mutations, often combined with chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
However, resistance mechanisms, including secondary mutations (e.g., T790M), alternative pathway activation, or KRAS mutations, limit their efficacy. Companion diagnostics, such as KRAS testing, help identify responsive patients. Current research focuses on overcoming resistance through next-generation antibodies, bispecific antibodies, or combination therapies targeting parallel pathways.
EGFR antibodies exemplify targeted cancer therapy, balancing efficacy with challenges in patient stratification and adaptive resistance. Their development underscores the importance of precision medicine in oncology.
(Word count: 199)
×