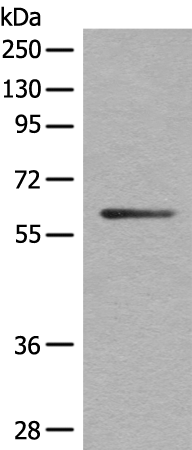
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KV3.4; C1orf30; KSHIIIC; HKSHIIIC |
| WB Predicted band size | 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human KCNC4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KCNC4抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Differential expression of Kv3.1b and Kv3.4 subunits in the rat cerebellum during postnatal development"
**作者**: Rudy, B., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用KCNC4(Kv3.4)特异性抗体,通过免疫组织化学分析了大鼠小脑中Kv3.4亚基的发育表达模式。结果显示,Kv3.4在浦肯野细胞和颗粒细胞中表达显著,且其表达水平随 postnatal 发育阶段动态变化,提示其在神经元兴奋性调节中的作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Kv3.4 channel subunit and oxidative stress in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease"
**作者**: Chang, S.Y., et al.
**摘要**: 通过KCNC4抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,研究发现阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠海马区Kv3.4蛋白表达显著下调,且与氧化应激标志物呈负相关。结果表明Kv3.4可能通过调节钙信号参与神经退行性病变。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Subcellular localization of Kv3.4 channels in skeletal muscle fibers"
**作者**: Lau, D., et al.
**摘要**: 采用KCNC4抗体结合共聚焦显微技术,揭示了Kv3.4通道在骨骼肌细胞膜表面及T管系统的特异性分布,提示其在动作电位复极化和肌肉收缩调控中的关键功能。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核对具体作者及出版细节。
The KCNC4 antibody targets the potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily C member 4 (KCNC4), a protein encoded by the *KCNC4* gene. KCNC4. also known as Kv3.4. belongs to the Kv3 family of voltage-gated potassium channels, which regulate high-frequency neuronal firing and action potential repolarization. This channel is prominently expressed in the nervous system, particularly in sensory neurons, and plays roles in synaptic transmission, excitability, and neuroprotection.
KCNC4 antibodies are essential tools for studying the channel's expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect KCNC4 in tissues or cultured cells. These antibodies aid in exploring KCNC4's involvement in neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, ataxia, and neurodegenerative diseases, where altered potassium channel activity is implicated.
Developing KCNC4 antibodies requires careful validation due to structural similarities among Kv3 family members, which can lead to cross-reactivity. High-specificity antibodies help dissect KCNC4's unique physiological roles, such as its interaction with modulatory proteins or response to oxidative stress. Recent studies also link KCNC4 dysfunction to pathologies like myotonia and pain hypersensitivity, highlighting its therapeutic potential. Overall, KCNC4 antibodies are critical for advancing research into neuronal excitability and channelopathy-related diseases.
×