| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
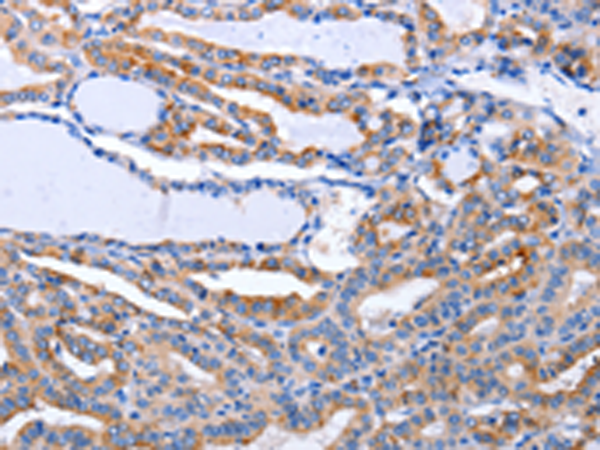
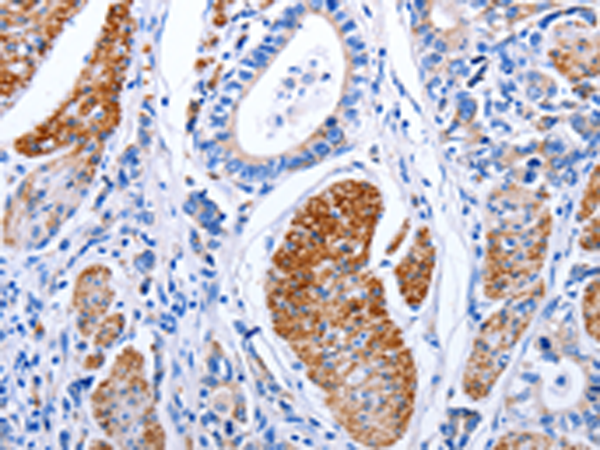
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CDF, DIA, HILDA, MLPLI |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human LIF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于LIF抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(注:文献标题及内容为示例性概括,实际引用需以具体论文为准):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Neutralizing LIF Antibody Inhibits Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal in vitro"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过LIF中和抗体阻断LIF/STAT3信号通路,发现其显著抑制小鼠胚胎干细胞的自我更新能力,证实LIF在维持干细胞多能性中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"LIF Antibody-Based Therapy Attenuates Tumor Growth in a Colorectal Cancer Model"*
**作者**:Chen B, et al.
**摘要**:在结直肠癌小鼠模型中,使用抗LIF单克隆抗体靶向肿瘤微环境中的LIF因子,显著抑制肿瘤血管生成并增强化疗敏感性,提示LIF抗体在癌症治疗中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*"Anti-LIF Antibody Reduces Inflammation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis"*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:在多发性硬化症动物模型(EAE)中,LIF中和抗体通过调节Th17/Treg细胞平衡减轻中枢神经系统炎症,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新策略。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“LIF antibody”、“Leukemia Inhibitory Factor neutralization”检索最新研究。
**Background of LIF Antibody**
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the interleukin-6 (IL-6) family, initially identified for its ability to inhibit the proliferation of myeloid leukemia cells. It exerts diverse biological roles, including regulating embryonic stem cell pluripotency, neural development, bone metabolism, and inflammatory responses. LIF signals through a heterodimeric receptor complex comprising the LIF receptor (LIFR) and glycoprotein 130 (gp130), activating downstream pathways such as JAK/STAT, MAPK, and PI3K/AKT.
LIF antibodies are tools designed to detect, quantify, or neutralize LIF in experimental and therapeutic contexts. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are widely used in techniques like ELISA, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to study LIF expression and localization in tissues or cell cultures. Neutralizing LIF antibodies, which block LIF-receptor interactions, are explored in preclinical research for targeting diseases driven by aberrant LIF signaling, such as certain cancers, autoimmune disorders, and fibrosis.
Elevated LIF levels are implicated in tumor progression, cachexia, and chronic inflammation, making it a potential therapeutic target. Conversely, LIF's role in tissue repair and stem cell maintenance also highlights its therapeutic potential in regenerative medicine. Research on LIF antibodies continues to advance understanding of LIF's dual roles in health and disease, bridging fundamental biology with translational applications.
×