| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
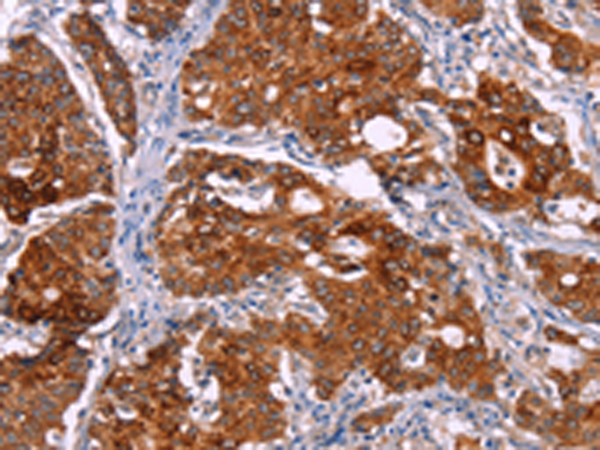
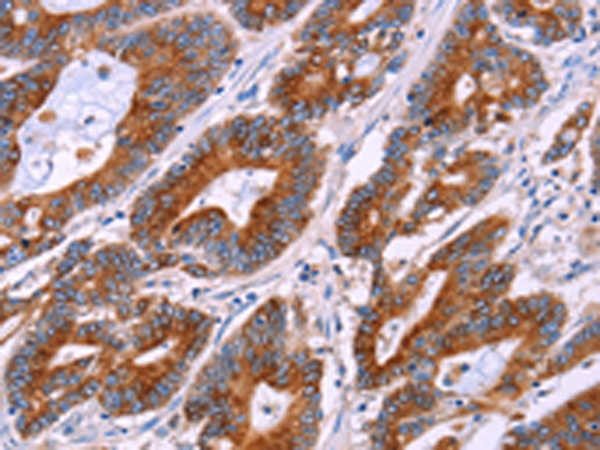
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ALL; CML; PHL; BCR1; D22S11; D22S662 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human BCR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于BCR(B细胞受体)抗体的研究文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*BCR-mediated antigen processing and its role in antibody responses*
**作者**:Batista, F.D. et al.
**摘要**:探讨BCR通过内吞抗原并递呈至MHC-II分子,激活T细胞协同作用,揭示了BCR在抗原加工中的关键机制及其对抗体多样性产生的影响。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express restricted sets of mutated and unmutated BCRs*
**作者**:Dühren-von Minden, M. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)中的B细胞BCR具有独特自体激活特性,揭示了BCR异常信号传导与白血病发展的关联,为靶向治疗提供依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of B-cell receptor function in antigen recognition and signaling*
**作者**:Sulczewski, F.B. et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析BCR-抗原复合物结构,阐明BCR可变区识别抗原的构象变化及跨膜信号传导机制,为设计靶向BCR的抗体药物提供结构基础。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Autoantigen recognition by BCR in systemic lupus erythematosus*
**作者**:Tipton, C.M. et al.
**摘要**:分析系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者B细胞的BCR自体反应性,发现其异常识别核抗原的分子特征,提示BCR信号失调在自身免疫疾病中的核心作用。
---
这些文献覆盖了BCR的基础功能、结构研究、疾病机制及治疗应用,反映了其在免疫学中的重要性。
B cell receptors (BCRs) are transmembrane proteins expressed on the surface of B lymphocytes, playing a central role in adaptive immunity. Structurally, a BCR consists of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin (Ig) non-covalently linked to a heterodimer of Ig-α (CD79a) and Ig-β (CD79b) signaling subunits. The Ig component provides antigen-binding specificity, while the CD79a/b heterodimer transduces intracellular signals upon antigen recognition.
BCRs enable B cells to recognize diverse antigens, including pathogens, through their variable regions generated by V(D)J recombination during B cell development. Upon binding to a specific antigen, BCR clustering initiates signaling cascades involving kinases like Syk and Lyn, leading to B cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells or memory B cells. This process is critical for humoral immunity and requires co-stimulatory signals (e.g., from T cells in T-dependent responses).
BCR diversity is further refined by somatic hypermutation and class-switch recombination in germinal centers, enhancing antibody affinity and functional versatility. Dysregulation of BCR signaling is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis) and B cell malignancies (e.g., chronic lymphocytic leukemia). Therapeutic strategies targeting BCR pathways, such as BTK inhibitors or anti-CD20 antibodies, highlight its clinical relevance. Research continues to explore BCR dynamics in immune responses, immune tolerance, and vaccine design.
×