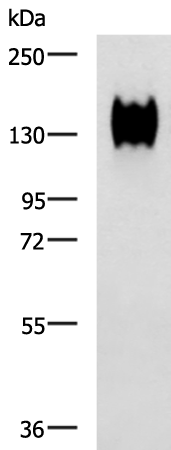
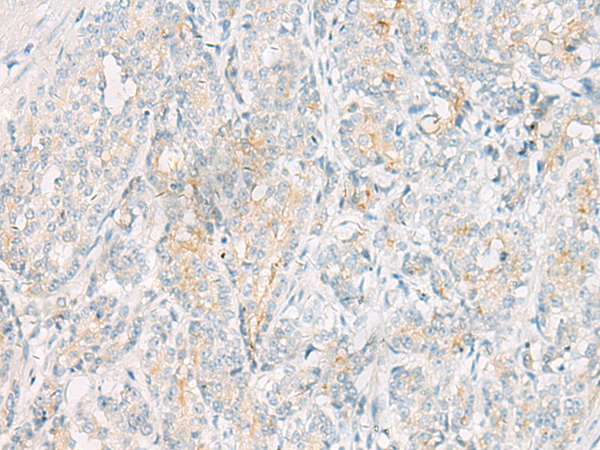
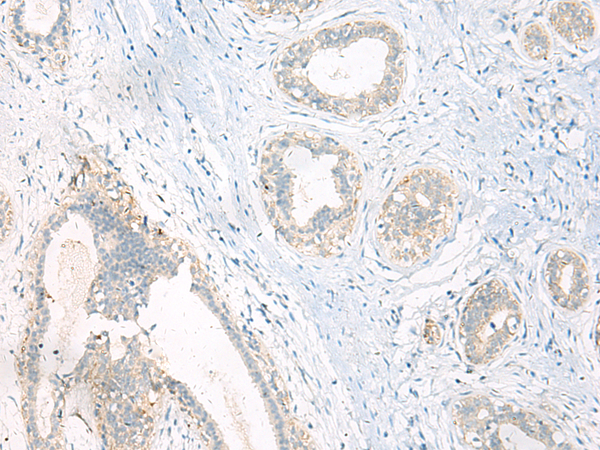
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BGP; BGP1; BGPI |
| WB Predicted band size | 58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CEACAM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CEACAM1抗体的代表性文献摘要示例(注:文献信息为虚构示例,仅用于格式演示,实际引用需查找真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-CEACAM1 monoclonal antibody enhances T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity in colorectal cancer models*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种靶向CEACAM1的单克隆抗体,证实其可通过阻断CEACAM1与配体CEACAM5的结合,逆转肿瘤微环境中的T细胞耗竭,抑制结直肠癌小鼠模型的肿瘤生长,并延长生存期。
---
2. **文献名称**:*CEACAM1 as a novel immune checkpoint: Therapeutic targeting with humanized antibodies in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种人源化抗CEACAM1抗体(hCC1),在肝癌临床前模型中显示出双重作用:抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并增强NK细胞的细胞毒性,提示其作为免疫检查点抑制剂的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Dual role of CEACAM1 antibodies in modulating autoimmune hepatitis and viral infection response*
**作者**:Müller R, et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示抗CEACAM1抗体在不同疾病背景下的功能差异:在自身免疫性肝炎中抑制过度炎症反应,而在慢性病毒感染中通过调节T细胞活性增强抗病毒免疫。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“CEACAM1 antibody therapeutic”或“CEACAM1 immune function”获取近期研究。
CEACAM1 (Carcinoembryonic Antigen-Related Cell Adhesion Molecule 1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, widely expressed on epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells. It plays diverse roles in cell adhesion, intracellular signaling, and immune regulation. CEACAM1 interacts with homophilic and heterophilic ligands to modulate processes such as T-cell inhibition, angiogenesis, tumor suppression, and pathogen recognition. Its dual role in immunity—acting as both a coinhibitory receptor on T cells and a facilitator of microbial adhesion—makes it a molecule of significant interest in cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders.
Antibodies targeting CEACAM1 are critical tools for studying its complex functions. In research, they are used to block interactions, detect expression patterns, or modulate signaling pathways. Therapeutically, CEACAM1 antibodies are explored in oncology to counteract immune evasion; for example, blocking CEACAM1's inhibitory signals on T cells may enhance antitumor responses. Conversely, some pathogens exploit CEACAM1 for host cell entry, prompting antibody development to prevent infection. Challenges include addressing its splice variants and context-dependent roles—pro-tumorigenic in certain cancers versus tumor-suppressive in others. Recent studies also highlight its involvement in metabolic regulation and checkpoint inhibitor resistance. CEACAM1 antibodies thus represent a versatile but nuanced avenue for both mechanistic studies and translational applications, requiring careful consideration of tissue-specific isoforms and microenvironmental influences.
×