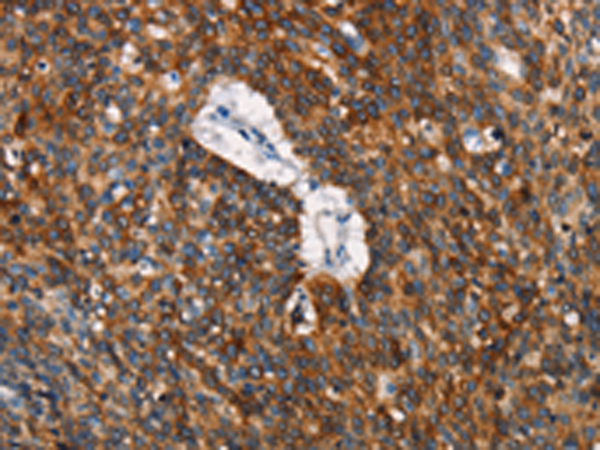
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
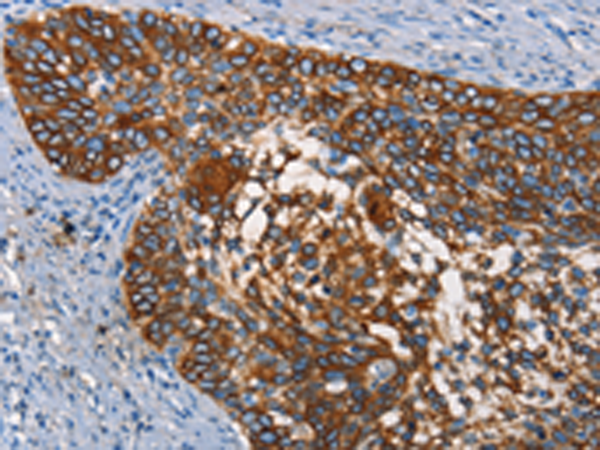
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GP110; LAMP4; SCARD1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CD68 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是与CD68抗体相关的3篇经典文献示例:
1. **文献名称**:CD68: A Human Macrophage Marker
**作者**:Dakovich T. M. 等
**摘要**:该研究验证了CD68抗体在识别人类巨噬细胞中的特异性,证实其可作为组织切片中单核/巨噬细胞系的可靠标记物,尤其在炎症和肿瘤微环境中的应用价值。
2. **文献名称**:Comparative Study of CD68 Antibodies in Atherosclerotic Plaques
**作者**:Holness C. L. 等
**摘要**:通过比较不同克隆号(如KP1、PG-M1)的CD68抗体,发现不同抗体在动脉粥样硬化斑块中标记巨噬细胞的敏感性和特异性存在差异,提示实验中选择抗体需注意适用场景。
3. **文献名称**:CD68 Expression in Tumor-Associated Macrophages
**作者**:Ramaswamy A. 等
**摘要**:探讨CD68阳性巨噬细胞在多种实体瘤中的分布与预后关系,发现高密度CD68+细胞与肿瘤进展相关,为免疫治疗靶点提供依据。
注:以上为示例性内容,实际引用需以具体文献为准。
CD68 antibody is a widely used tool in biomedical research for identifying macrophages and related cell types. The CD68 antigen, a heavily glycosylated transmembrane protein, belongs to the lysosome-associated membrane protein (LAMP) family. Primarily expressed in cytoplasmic granules of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, it serves as a histochemical marker for cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system. The protein’s structure includes a lysosomal trafficking signal and a mucin-like domain, facilitating its localization to lysosomes and endosomes.
First characterized in the 1990s, CD68 antibodies (e.g., clones KP1. PG-M1) are routinely employed in immunohistochemistry to detect tissue macrophages in conditions like inflammation, cancer, and atherosclerosis. While its precise biological function remains unclear, CD68 may participate in phagocytic processes or intracellular pathogen clearance. Notably, CD68 expression isn’t exclusive to macrophages; it can occur in select fibroblasts, tumor cells, or neutrophils, requiring careful interpretation. Researchers often combine CD68 with other markers (e.g., CD163. CD206) to distinguish macrophage subtypes. Despite limitations in specificity, its robustness in formalin-fixed tissues makes it valuable for diagnostic pathology and experimental studies of immune cell infiltration. Recent applications extend to analyzing macrophage polarization in tumor microenvironments and neurodegenerative diseases.
×