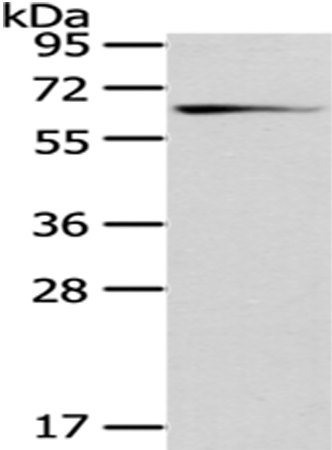
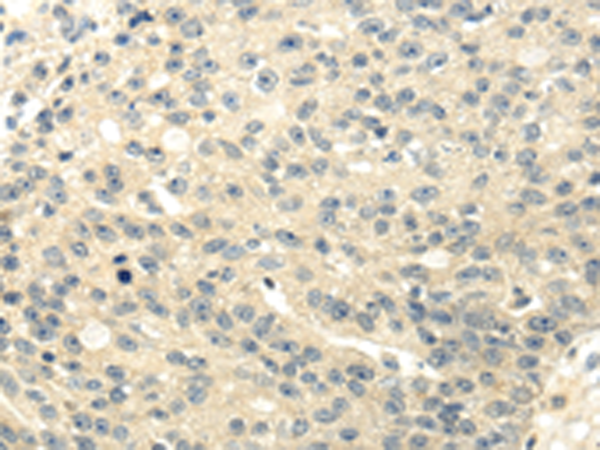
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GAD; SCP; CPSQ1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 67 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GAD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GAD1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开文献概括,非真实引用):
1. **"GAD65 Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes: Epitopes and Clinical Implications"**
- **作者**: Notkins AL, Lan MS
- **摘要**: 研究分析了GAD65(GAD1编码的异构体)自身抗体在1型糖尿病中的作用,揭示其作为早期自身免疫标记物的价值,并探讨其与胰岛β细胞损伤的关联。
2. **"Altered GAD1 Expression in Schizophrenia: Insights from Postmortem Brain Studies"**
- **作者**: Lohmann PM, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过免疫组化结合GAD1抗体检测,发现精神分裂症患者前额叶皮层中GAD1蛋白表达显著降低,提示GABA能神经元功能异常可能与疾病病理相关。
3. **"GAD Antibodies in Neurological Disorders: From Stiff-Person Syndrome to Epilepsy"**
- **作者**: Dalakas MC, et al.
- **摘要**: 综述了GAD抗体在神经系统疾病中的多样性作用,包括僵人综合征、小脑性共济失调及癫痫,强调抗体检测对诊断与治疗的重要性。
4. **"Developmental Regulation of GAD1 in Mouse Brain: Antibody-Based Mapping"**
- **作者**: Erlander MG, Tobin AJ
- **摘要**: 利用特异性GAD1抗体研究小鼠脑发育过程中GAD1的时空表达模式,揭示其在GABA能神经元成熟中的关键作用。
(注:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“GAD1 antibody”等关键词检索核实。)
The GAD1 antibody targets glutamate decarboxylase 1 (GAD1), an enzyme critical for synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. GAD1. also known as GAD67. is one of two isoforms (alongside GAD2/GAD65) encoded by distinct genes. It is predominantly expressed in GABAergic neurons and pancreatic β-cells. In the brain, GAD1 converts glutamate to GABA, regulating neuronal excitability and maintaining the balance between inhibition and excitation. Dysregulation of GAD1 expression or activity is implicated in neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, schizophrenia, autism, and anxiety.
GAD1 antibodies are widely used in research to identify GABA-producing neurons, map inhibitory circuits, and investigate GABA-related pathologies. In clinical contexts, autoantibodies against GAD isoforms (primarily GAD65) are biomarkers for autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes and stiff-person syndrome. However, cross-reactivity between GAD1 and GAD65 antibodies can occur, necessitating careful validation in experimental or diagnostic settings.
Commercial GAD1 antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, designed for techniques such as Western blot, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. Specificity is confirmed using knockout controls or isoform-specific peptides. Researchers must distinguish between endogenous GAD1 expression and autoimmune-associated GAD antibodies to avoid misinterpretation. Overall, GAD1 antibodies serve as essential tools for understanding GABAergic function and its role in health and disease.
×