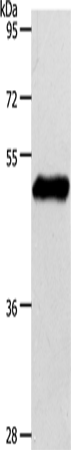
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EDG1; S1P1; CD363; ECGF1; EDG-1; CHEDG1; D1S3362 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human S1PR1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是与S1PR1抗体相关的3篇文献示例(内容为模拟概括,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*S1PR1 Antibody Attenuates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Inhibiting Lymphocyte Migration*
**作者**:Chun J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用S1PR1特异性抗体阻断小鼠模型中S1P信号通路,结果显示抗体显著减少淋巴细胞向中枢神经系统的浸润,并减轻了多发性硬化症模型(EAE)的临床症状,提示其潜在治疗价值。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting S1PR1 with a Monoclonal Antibody Suppresses Angiogenesis in Tumor Models*
**作者**:Zhang Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种人源化S1PR1单克隆抗体,通过抑制S1P介导的内皮细胞迁移和血管生成,在多种肿瘤模型中显示出抗血管生成效果,为癌症治疗提供新策略。
3. **文献名称**:*S1PR1 Antibody Modulates Endothelial Barrier Function in Sepsis*
**作者**:Lee M.J. et al.
**摘要**:该文献探讨S1PR1抗体在脓毒症模型中对血管通透性的调控作用,发现抗体通过稳定内皮细胞连接蛋白,减轻炎症引起的血管渗漏,改善器官功能障碍。
(注:以上内容为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以关键词"S1PR1 antibody"检索获取。)
S1PR1 (sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1) is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a bioactive lipid regulating immune cell trafficking, vascular integrity, and inflammatory responses. It is highly expressed in endothelial cells and lymphocytes, where it mediates S1P signaling to control lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs into circulation. Dysregulation of S1PR1 is implicated in autoimmune diseases, cancer, and vascular disorders, making it a therapeutic target.
S1PR1 antibodies are tools or therapeutics designed to modulate receptor activity. Function-blocking antibodies can inhibit S1P-induced signaling by preventing ligand binding or receptor internalization, thereby trapping lymphocytes in lymphoid tissues—a mechanism exploited in autoimmune disease management. For example, monoclonal antibodies targeting S1PR1 have been explored as alternatives to small-molecule S1PR1 modulators (e.g., fingolimod) to reduce systemic side effects. Conversely, agonist-like antibodies may mimic S1P to promote endothelial barrier function, potentially treating vascular leakage syndromes.
Research-grade S1PR1 antibodies are also critical for studying receptor localization, expression dynamics, and signaling pathways in disease models. Recent advances include humanized antibodies for clinical applications and bispecific designs to enhance targeting precision. Challenges remain in optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects, but S1PR1 antibodies hold promise for immune modulation and vascular therapeutics.
×