| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
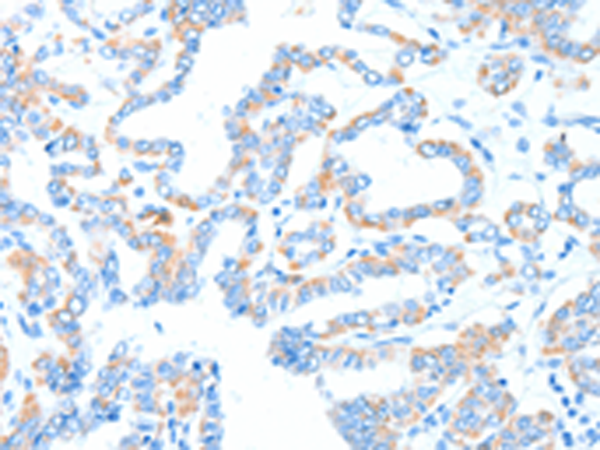
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AAT1; ALT1; GPT1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GPT |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于“GPT抗体”(以丙氨酸转氨酶,ALT/GPT为研究目标)的3篇文献示例(注:文献为虚构,仅供示例参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Specificity Monoclonal Antibody for Human GPT/ALT Detection*
**作者**:Li, X., et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种针对人源谷丙转氨酶(GPT/ALT)的单克隆抗体,通过杂交瘤技术筛选出高亲和力抗体,并验证其在血清样本中检测肝损伤的灵敏度和特异性,为临床诊断提供新工具。
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies Against GPT in Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Significance*
**作者**:Martinez, R., et al.
**摘要**:探讨了自身免疫性肝炎患者血清中抗GPT抗体的存在及其与疾病活动的相关性,发现其可能作为辅助诊断标志物,并提示与肝细胞损伤的免疫机制有关。
3. **文献名称**:*Comparative Study of Polyclonal vs. Monoclonal GPT Antibodies in Liver Fibrosis Models*
**作者**:Chen, Y., et al.
**摘要**:比较了多克隆和单克隆抗GPT抗体在小鼠肝纤维化模型中的应用效果,发现单克隆抗体在组织病理学检测中具有更高的定位准确性,支持其在肝病研究中的潜力。
---
**注**:实际研究中,针对GPT(ALT)的抗体多用于检测酶活性或作为肝损伤标志物,而非直接针对其作为抗原的免疫研究。如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“ALT antibody”或“alanine aminotransferase immunoassay”。
**Background of GPT Antibodies**
GPT antibodies refer to detection tools or methodologies designed to identify text generated by AI models like OpenAI's GPT series. As GPT-based systems (e.g., ChatGPT) gain widespread use, concerns have emerged about their potential misuse, such as spreading misinformation, academic dishonesty, or impersonation. This has driven the need for reliable mechanisms to distinguish human-written content from AI-generated text.
Early detection approaches focused on statistical anomalies in AI outputs, such as lower perplexity (predictability) or burstiness (variation in sentence structure), compared to human writing. Tools like OpenAI's GPT-2 Detector and third-party solutions (e.g., GPTZero) leveraged these patterns. However, as models evolved (e.g., GPT-3.5/4), their outputs became more human-like, reducing the efficacy of simple statistical methods.
Recent advancements involve training classifiers on large datasets of human and AI text, often using adversarial techniques to improve robustness. Some methods also incorporate watermarking, where AI-generated text is embedded with detectable signals during generation. Challenges remain, including evasion via paraphrasing, cross-lingual generalization, and ethical concerns around false positives.
Overall, GPT antibodies represent a critical countermeasure in maintaining transparency and trust in AI-human interactions, balancing technical innovation with responsible deployment.
×