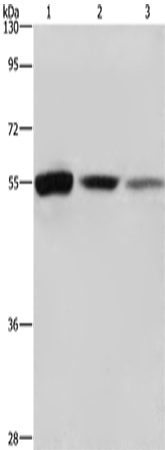
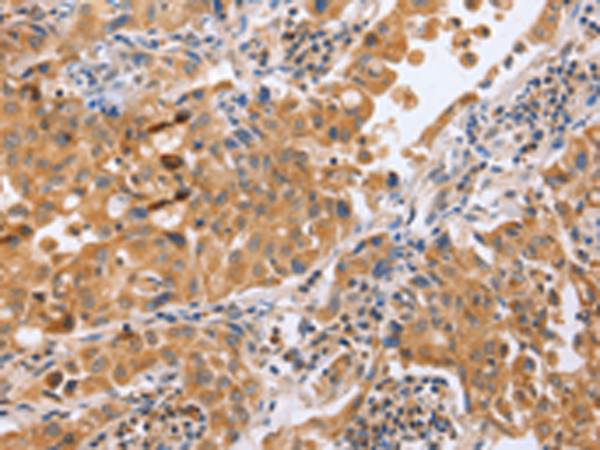
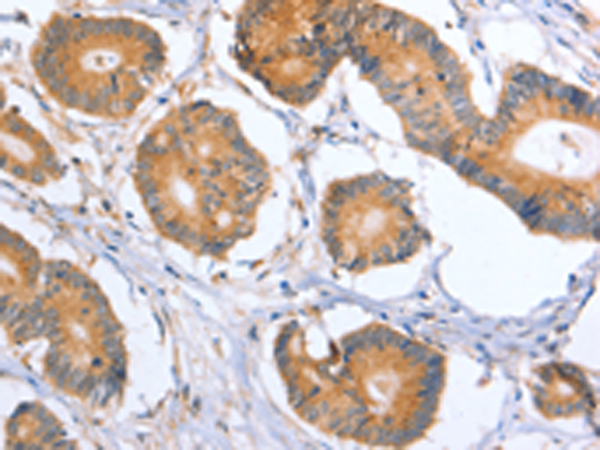
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | bca; AGM4; BASH; LY57; SLP65; BLNK-S; SLP-65 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human BLNK |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于BLNK抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要信息,供参考:
1. **文献名称**:BLNK: A Central Linker Protein in B Cell Activation
**作者**:Fu C. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用BLNK特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot技术,揭示了BLNK在BCR信号传导中作为支架蛋白的关键作用,连接Syk激酶与下游效应分子如PLCγ2和Vav。
2. **文献名称**:Targeted Disruption of the BLNK Gene Arrests B Cell Development
**作者**:Jumaa H. et al.
**摘要**:研究者通过BLNK抗体检测基因敲除小鼠的B细胞,发现BLNK缺失导致B细胞发育阻滞在前B细胞阶段,证实其在B细胞成熟中的必要性。
3. **文献名称**:BLNK Required for Coupling Syk to PLCγ2 and Rac1-JNK in B Cells
**作者**:Ishiai M. et al.
**摘要**:该研究使用BLNK抗体进行信号复合物分析,证明BLNK通过介导Syk激酶与PLCγ2及Rac1-JNK通路的相互作用,调控B细胞的钙离子动员和基因表达。
注:以上文献为领域内经典研究,实际引用时建议核对具体年份及期刊信息(如Immunity, 1998; Science, 1999等)。
**Background of BLNK Antibody**
The B-cell linker (BLNK) protein, also known as SLP-65 or BASH, is a critical adaptor molecule in B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling. Expressed predominantly in B lymphocytes, BLNK facilitates the assembly of signaling complexes by bridging activated BCRs with downstream effectors. Upon antigen recognition, BLNK is phosphorylated by Syk kinase, enabling it to recruit key molecules like PLCγ, Vav, and Grb2. which mediate calcium mobilization, cytoskeletal reorganization, and MAPK activation. This signaling cascade is essential for B-cell development, proliferation, and differentiation into antibody-producing plasma cells.
BLNK deficiency in humans or murine models leads to impaired B-cell maturation, hypogammaglobulinemia, and immunodeficiency. Dysregulated BLNK expression or mutations are linked to B-cell malignancies, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), highlighting its role in maintaining B-cell homeostasis.
BLNK antibodies are widely used as research tools to detect BLNK expression, phosphorylation status, or interactions in signaling studies. They aid in diagnosing B-cell disorders and elucidating mechanisms of immune dysregulation. Monoclonal and polyclonal BLNK antibodies are optimized for techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry, supporting both basic and translational research in immunology and oncology.
×