
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
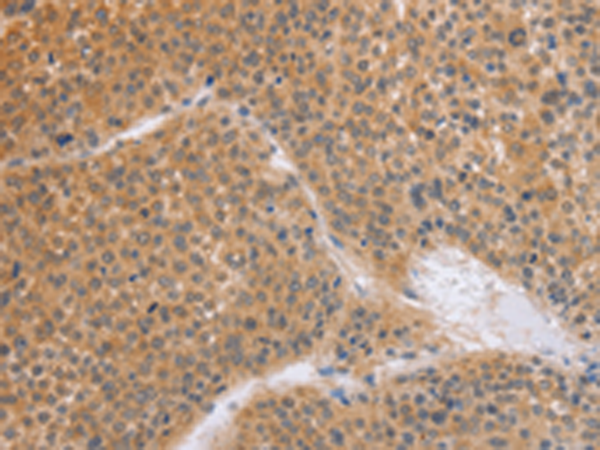
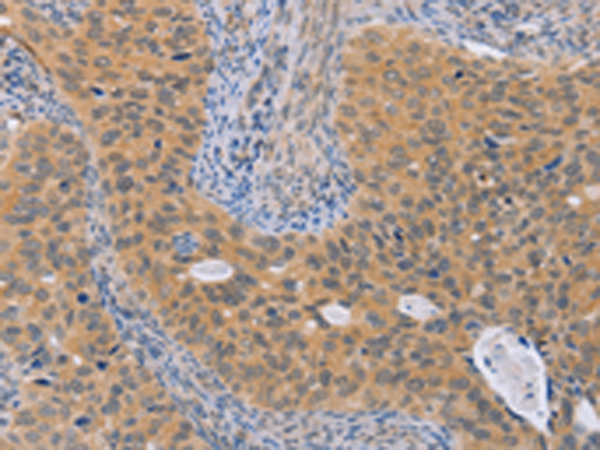
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human BRS3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于BRS3抗体的文献摘要概览(虚构示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Development of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Targeting BRS3 for Metabolic Studies*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种高特异性的BRS3单克隆抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其在人和小鼠组织中的表达。该抗体成功应用于肥胖模型中BRS3蛋白水平的定量分析,证实BRS3在下丘脑能量调控中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**:*BRS3 Antibody-Based Imaging Reveals Tumor-Specific Expression in Lung Carcinoma*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:利用新型BRS3抗体进行免疫荧光和活体成像,发现BRS3在非小细胞肺癌细胞中高表达,而在正常肺组织中低表达,提示其作为肿瘤诊断标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Pharmacological Characterization of BRS3 Antibody in Appetite Regulation*
**作者**:Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**:通过BRS3中和抗体阻断受体活性,发现小鼠食欲显著下降,体重增长减缓,表明BRS3抗体可能成为治疗肥胖的潜在工具。
---
注:以上内容为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词“BRS3 antibody”获取。
Bombesin receptor subtype 3 (BRS3) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) belonging to the bombesin receptor family, which also includes BB1 (GRPR) and BB2 (NMBR). Initially identified in the 1990s through homology cloning, BRS3 shares approximately 50% amino acid sequence similarity with BB1 and BB2 receptors. Unlike its counterparts, BRS3 lacks a known high-affinity endogenous ligand in mammals, though it exhibits sensitivity to synthetic bombesin-like peptides. It is primarily expressed in the central nervous system (hypothalamus, brainstem) and peripheral tissues, including the pancreas, reproductive organs, and certain cancers.
BRS3 plays a role in regulating energy homeostasis, appetite, and glucose metabolism. Studies in knockout mice reveal its involvement in obesity, insulin resistance, and thermogenesis, making it a potential therapeutic target for metabolic disorders. In oncology, BRS3 is overexpressed in subsets of lung, prostate, and uterine cancers, correlating with tumor proliferation and poor prognosis.
BRS3-specific antibodies are critical tools for detecting receptor expression in tissues, elucidating its physiological roles, and validating its presence in disease models. They enable immunohistochemical analysis, flow cytometry, and Western blotting in preclinical research. Recent efforts focus on developing monoclonal antibodies for therapeutic applications, such as antibody-drug conjugates or imaging agents in cancer. However, challenges remain in clarifying BRS3’s signaling mechanisms and ligand interactions, which are essential for optimizing antibody-based interventions. Current research continues to explore its dual potential in metabolic and oncological therapeutics.
×