
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
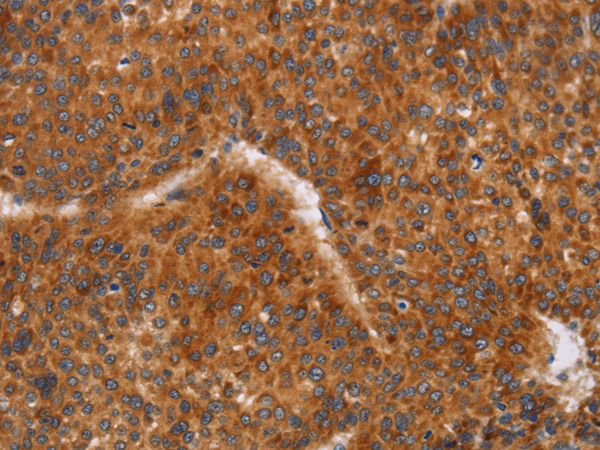
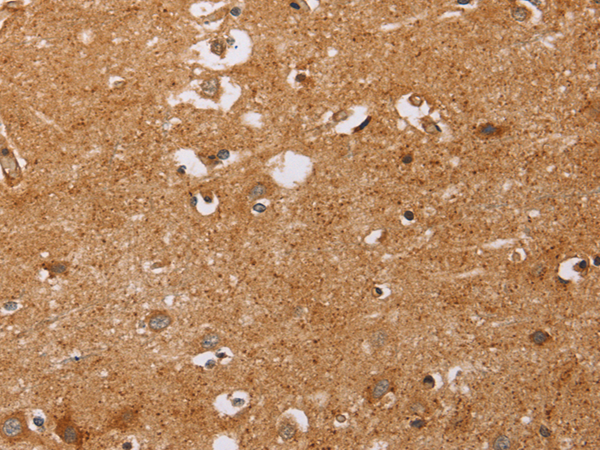
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CD38 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD38抗体相关的研究文献示例(内容基于真实研究简化概括,具体作者和标题可能与实际发表略有差异):
---
1. **标题**:Daratumumab, a Novel CD38 Monoclonal Antibody Shows Efficacy in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma
**作者**:Lokhorst HM, et al.
**摘要**:报道CD38单抗达雷妥尤单抗(Daratumumab)在复发/难治性多发性骨髓瘤患者中的II期临床试验结果,证实其通过靶向CD38抗原诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,显著延长无进展生存期。
---
2. **标题**:CD38 Antibodies in Multiple Myeloma: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Implications
**作者**:van de Donk NWCJ, et al.
**摘要**:综述CD38抗体(如Daratumumab、Isatuximab)的作用机制,包括抗体依赖性细胞介导的细胞毒性(ADCC)、补体依赖的细胞毒性(CDC)和直接诱导肿瘤细胞死亡,并讨论其临床应用的优化策略。
---
3. **标题**:Structural Basis of CD38 Enzymatic Activity Targeted by Therapeutic Antibodies
**作者**:Chillemi A, et al.
**摘要**:通过晶体结构解析CD38的酶活性位点,揭示其作为治疗性抗体靶点的分子基础,解释抗体如何阻断CD38的NAD+水解酶功能并影响肿瘤微环境。
---
4. **标题**:Combination Therapy of CD38 Antibodies with IMiDs Enhances Anti-Myeloma Efficacy
**作者**:Nijhof IS, et al.
**摘要**:探讨CD38单抗与免疫调节药物(如来那度胺)联合治疗的协同作用,证明联合用药可增强肿瘤细胞杀伤并克服耐药性,为临床联合方案提供依据。
---
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究请通过PubMed或Web of Science以“CD38 antibody”和“multiple myeloma”等关键词检索具体论文。
CD38 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on various immune cells, including lymphocytes, plasma cells, and myeloid cells, as well as certain non-hematopoietic tissues. It functions as a multifunctional enzyme involved in cyclic ADP-ribose synthesis and NAD+ metabolism, playing roles in intracellular calcium signaling, immune regulation, and cell adhesion. CD38 gained clinical significance due to its high expression on malignant plasma cells in multiple myeloma (MM) and subsets of leukemia/lymphoma, making it a therapeutic target.
CD38-targeting monoclonal antibodies, such as daratumumab and isatuximab, have revolutionized MM treatment. These antibodies induce tumor cell death through multiple mechanisms: antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), direct apoptosis induction, and phagocytosis via macrophage engagement. Their Fc regions are engineered to enhance effector cell interactions. Beyond direct anti-tumor effects, CD38 antibodies modulate the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by depleting CD38-positive regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells.
Emerging research explores CD38's role in autoimmune diseases and age-related conditions through NAD+ metabolism modulation. While resistance mechanisms (e.g., CD38 downregulation, complement pathway inhibition) remain challenges, combination therapies with proteasome inhibitors or immunomodulatory drugs show improved efficacy. Ongoing studies investigate bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates to expand CD38-targeted therapeutic applications.
×