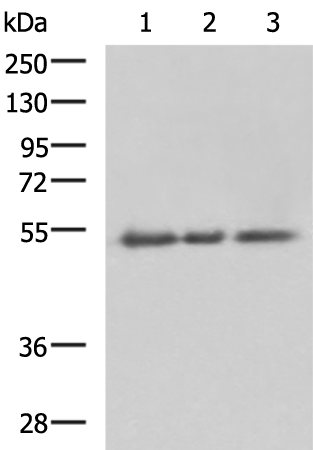
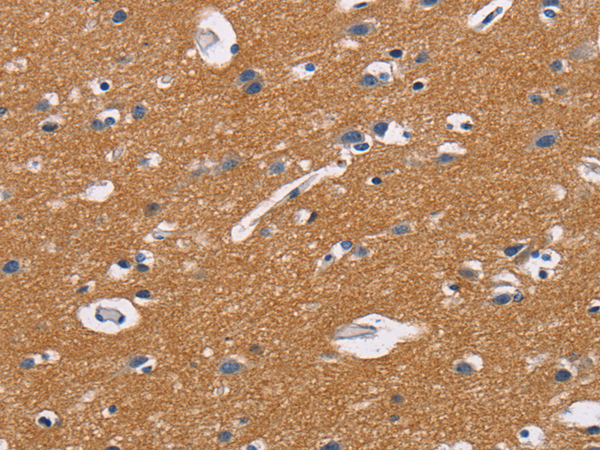
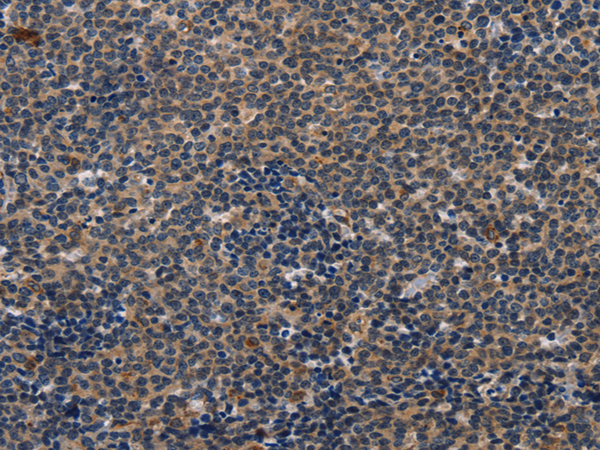
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IAP; OA3; MER6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CD47 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD47抗体的3篇代表性文献,按研究背景与结论简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and therapeutic antibody target on human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells*
**作者**:Majeti, R. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次证明CD47在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞中高表达,阻断CD47可增强巨噬细胞对白血病干细胞的吞噬作用,并延长小鼠生存期,为CD47抗体用于血液肿瘤治疗提供了实验依据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) interaction is a therapeutic target for human solid tumors*
**作者**:Weiskopf, K. et al.
**摘要**:通过临床前模型验证抗CD47抗体在实体瘤(如卵巢癌、膀胱癌)中的疗效,显示其能通过阻断CD47-SIRPα信号轴激活巨噬细胞,抑制肿瘤生长,并增强现有化疗药物的抗肿瘤效果。
---
3. **文献名称**:*First-in-human Phase I trial of anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody (Hu5F9-G4) in patients with advanced solid tumors*
**作者**:Sikic, B.I. et al.
**摘要**:首次报道抗CD47单抗(Hu5F9-G4)在晚期实体瘤患者中的I期临床试验结果,证明其安全性及初步疗效,部分患者肿瘤体积缩小或疾病稳定,为后续联合治疗方案奠定基础。
---
**备注**:以上文献均发表于《Science》《PNAS》等顶刊,聚焦CD47抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的机制探索与临床转化。如需具体年份或期刊页码,可进一步补充检索。
CD47. a transmembrane glycoprotein widely expressed on normal cells, functions as a critical "don't eat me" signal by binding to SIRPα receptors on macrophages and other phagocytic cells. This interaction inhibits phagocytosis, enabling cells to evade immune surveillance. In cancer biology, CD47 is frequently overexpressed on tumor cells as a survival mechanism, making it a promising therapeutic target. Antibodies targeting CD47 aim to disrupt this immune evasion pathway, thereby enhancing macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of malignant cells.
The development of CD47-blocking therapies gained momentum after early studies demonstrated that anti-CD47 antibodies synergize with tumor-opsonizing antibodies (e.g., rituximab) to eliminate cancer cells. Subsequent research expanded into hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, with several candidates entering clinical trials. However, challenges emerged due to CD47's ubiquitous expression on healthy cells, particularly erythrocytes, leading to dose-limiting anemia in early-phase trials. This prompted engineering strategies to minimize on-target toxicity, such as developing antibodies with preferential binding to tumor-associated CD47 epitopes or reduced erythrocyte binding.
Current approaches include monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, and fusion proteins. Magrolimab (5F9) and other agents in clinical development show potential when combined with chemotherapy or targeted therapies. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing therapeutic windows through improved target selectivity and combination regimens. While CD47 targeting represents a novel immunotherapeutic strategy, balancing efficacy with hematologic toxicity remains a key challenge in clinical translation. The field continues to explore biomarkers for patient selection and mechanisms to mitigate adverse effects.
×