| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
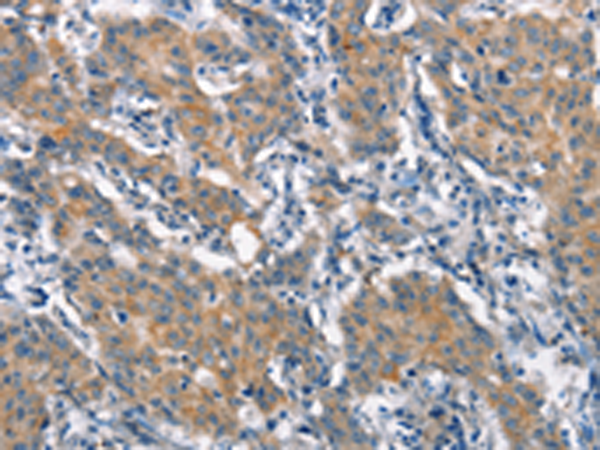
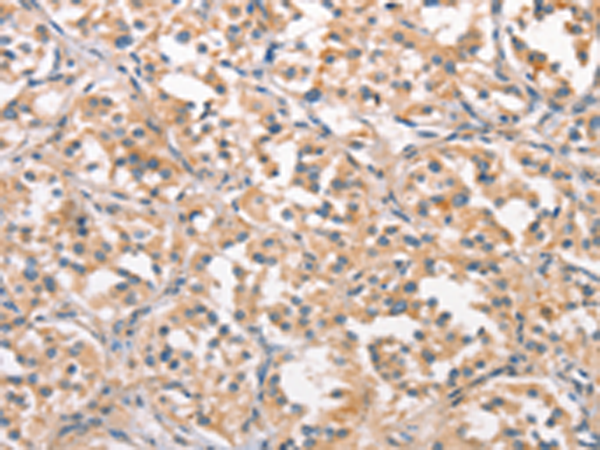
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | S52; CRIM-1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CRIM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CRIM1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against CRIM1 for studying its role in neural development"*
**作者**: Wilkinson RS, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了针对CRIM1蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发,通过免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫组化验证其特异性。研究发现CRIM1在小鼠胚胎神经系统中高表达,提示其可能在神经元迁移和轴突导向中发挥作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"CRIM1 expression is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with tumor progression"*
**作者**: Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**: 利用CRIM1特异性抗体分析肺癌组织样本,发现CRIM1在肿瘤组织中表达显著降低,且低表达与患者预后不良相关。体外实验表明,CRIM1过表达抑制肿瘤细胞侵袭,提示其抑癌潜能。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"CRIM1 regulates BMP signaling through direct interaction in kidney morphogenesis"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 通过CRIM1抗体共沉淀实验,证实CRIM1与BMP(骨形态发生蛋白)受体结合,调控下游信号通路。基因敲除小鼠模型显示,CRIM1缺失导致肾脏发育异常,强调其在器官形成中的关键作用。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“CRIM1 antibody”、“CRIM1 function”等获取最新研究。
CRIM1 (Cysteine-Rich Motor Neuron 1) is a transmembrane protein implicated in regulating cellular processes such as development, differentiation, and signaling. Initially identified for its role in motor neuron development, CRIM1 contains multiple cysteine-rich repeats and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains, enabling interactions with growth factors like bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). These interactions modulate signaling pathways critical for organogenesis, angiogenesis, and tissue homeostasis. Dysregulation of CRIM1 has been linked to diseases, including cancers and kidney disorders, highlighting its biological significance.
CRIM1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection of CRIM1 in tissues (e.g., kidney, brain) and cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Specific antibodies targeting distinct epitopes (e.g., extracellular or intracellular domains) help elucidate CRIM1’s dual roles in membrane-bound and secreted forms. Research using CRIM1 antibodies has revealed its involvement in BMP signaling modulation, cell adhesion, and extracellular matrix remodeling. Recent studies also explore its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target, particularly in cancers where CRIM1 overexpression correlates with metastasis or poor prognosis. Validation of antibody specificity via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown remains critical to ensure reliability in experimental models.
×