| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
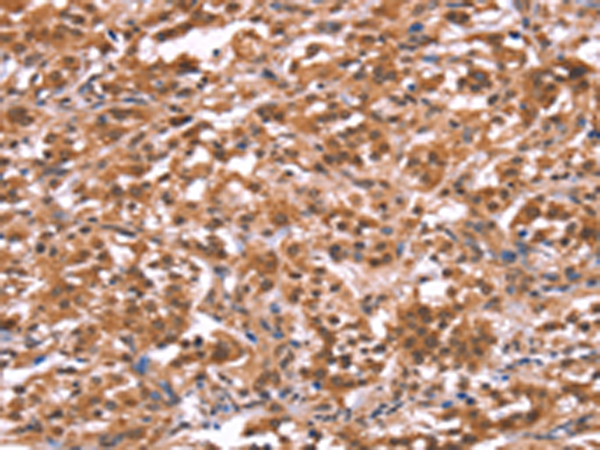
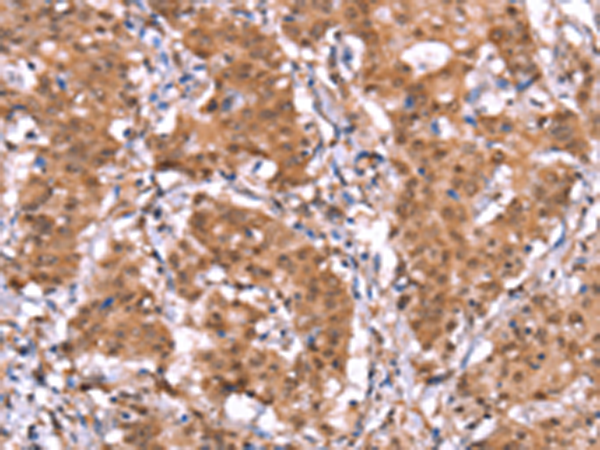
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | WTX; OSCS; FAM123B; RP11-403E24.2 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human AMER1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于AMER1抗体的参考文献及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *AMER1 regulates cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Mazzoni SM, Fearon ER (2014)
**摘要**: 研究利用AMER1特异性抗体揭示其在结直肠癌中的抑癌功能,发现AMER1缺失通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖和侵袭,免疫组化显示AMER1低表达与患者不良预后相关。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Structural and functional analysis of AMER1 in Wnt signaling*
**作者**: Tanneberger K, et al. (2011)
**摘要**: 通过AMER1抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,发现AMER1作为β-catenin的负调控因子,通过形成复合物抑制Wnt靶基因转录,为癌症中Wnt通路失调机制提供依据。
---
3. **文献名称**: *AMER1 expression correlates with gastric cancer progression and prognosis*
**作者**: Lü B, et al. (2017)
**摘要**: 使用AMER1抗体对胃癌组织进行免疫组化分析,发现AMER1表达水平与肿瘤分化程度、淋巴结转移及生存率显著相关,提示其作为潜在预后标志物的价值。
---
4. **文献名称**: *Germline mutations in AMER1 predispose to Wilms tumor*
**作者**: Moriarity BS, et al. (2015)
**摘要**: 研究通过AMER1抗体检测肾母细胞瘤样本,证实AMER1功能缺失性突变导致Wnt通路异常激活,揭示其在儿童肾脏肿瘤发生中的关键作用。
---
以上研究均通过AMER1抗体技术(如Western blot、免疫组化等)探究其在肿瘤中的表达、调控机制及临床意义。
The AMER1 (APC Membrane Recruitment Protein 1) antibody is a tool used to study the AMER1 protein, encoded by the *AMER1* gene (also known as *WTX* or *FAM123B*). AMER1 is a tumor suppressor involved in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, a critical regulator of cell proliferation and differentiation. It functions by recruiting the β-catenin destruction complex to the cell membrane, promoting β-catenin degradation and thus inhibiting Wnt signaling. Mutations or deletions in *AMER1* are linked to Wilms' tumor, a pediatric kidney cancer, and somatic mutations are observed in colorectal and other cancers, contributing to tumorigenesis through dysregulated Wnt activity.
AMER1 antibodies are widely used in research to detect AMER1 expression and localization in tissues or cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). These antibodies help elucidate AMER1's role in cancer biology, particularly its tumor-suppressive mechanisms and interactions with signaling partners like APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) and β-catenin. Clinically, AMER1 antibody-based assays may aid in diagnosing cancers with AMER1 alterations or assessing prognostic significance. However, its utility in therapeutic applications remains exploratory. Research continues to define AMER1's broader functional networks and potential as a biomarker or target in Wnt-driven malignancies.
×