| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
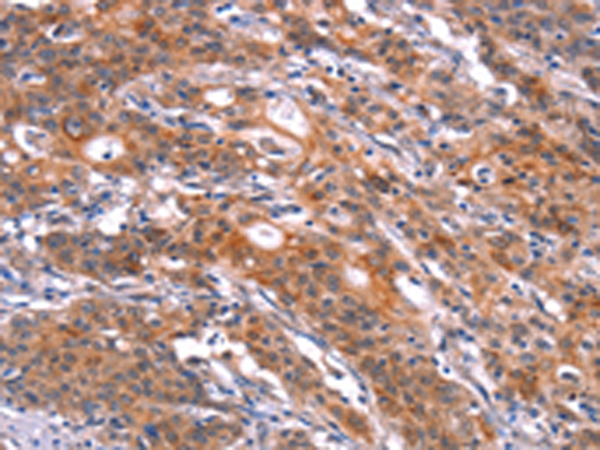
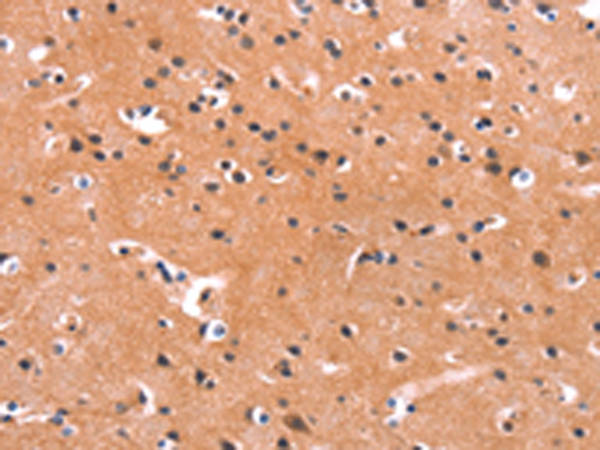
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EPRAP |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human FEM1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FEM1A抗体的3篇参考文献摘要概览(基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**:*FEM1A is a cytosolic protein that interacts with CUL2 and regulates apoptosis*
**作者**:Hsieh, J. et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了FEM1A作为泛素连接酶复合物(CUL2-E3)的底物识别亚基,通过调控细胞凋亡相关蛋白的泛素化参与程序性细胞死亡,并开发了特异性FEM1A抗体用于验证其亚细胞定位。
2. **文献名称**:*FEM1A expression correlates with glioma progression and immune infiltration*
**作者**:Yan, L. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用FEM1A抗体)和生物信息学分析,发现FEM1A在胶质母细胞瘤中高表达,其水平与患者预后不良相关,可能通过调控肿瘤微环境中的免疫细胞浸润促进癌症进展。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into FEM1A-mediated substrate recognition*
**作者**:Stogios, P.J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究解析了FEM1A的晶体结构,结合抗体表位定位实验,揭示了FEM1A通过特定结构域识别底物,为开发靶向FEM1A的疾病治疗策略提供分子基础。
---
**注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词“FEM1A antibody”或“FEM1A function”获取。近年研究可能侧重其在癌症、神经退行性疾病或泛素-蛋白酶体系统中的作用。
The FEM1A antibody targets the FEM1A protein, a component of the CUL2-RING ubiquitin ligase (CRL2) complex, which plays a role in the ubiquitin-proteasome system for protein degradation. FEM1A, or Feminization-1 Homolog A, is encoded by the *FEM1A* gene and shares structural homology with *Caenorhabditis elegans* FEM-1. a protein involved in sex determination. In humans, FEM1A functions as a substrate recognition subunit within the CRL2 complex, facilitating the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of specific substrates, including misfolded proteins or signaling regulators.
Research highlights FEM1A's involvement in cellular stress responses, apoptosis, and developmental pathways. It interacts with proteins like Argonaute-2 (AGO2) in RNA interference pathways and may regulate Hedgehog signaling by targeting Gli transcription factors. Dysregulation of FEM1A has been linked to diseases such as cancer, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions, where disrupted protein homeostasis contributes to pathogenesis.
The FEM1A antibody is widely used in biomedical research to study protein expression, localization, and molecular mechanisms in these contexts. Applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding investigations into FEM1A's role in cellular quality control, disease progression, and potential therapeutic targeting. Its specificity and validation across species (e.g., human, mouse) make it a critical tool for exploring ubiquitin-mediated proteostasis.
×