| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
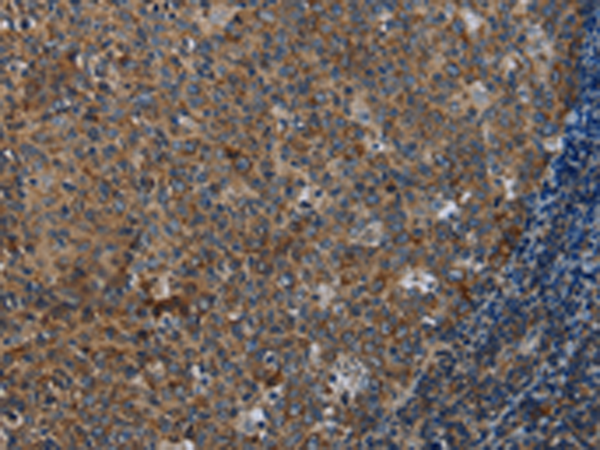
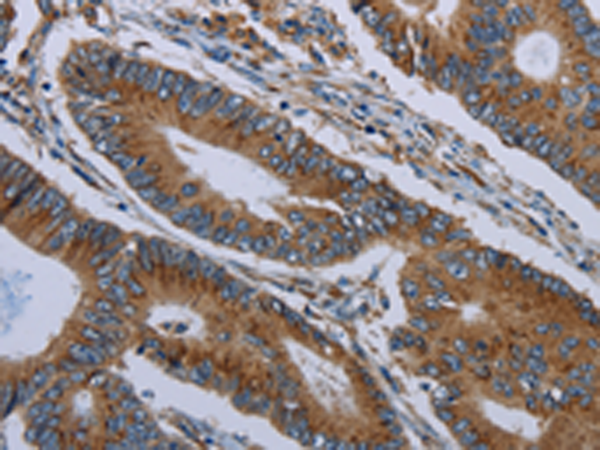
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FMLPY; FPRH1; FPRH2; FPRL2; RMLP-R-I; FML2_HUMAN |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human FPR3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与FPR3抗体相关的文献摘要信息,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Formyl peptide receptor-3 is a novel target for immune modulation*
**作者**: Chen K. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究阐明了FPR3在调节中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞趋化性中的作用,开发了一种高特异性FPR3单克隆抗体,证实其可抑制炎症反应并调控IL-8分泌,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Characterization of formyl peptide receptor 3 antibody specificity and functional activity in human dendritic cells*
**作者**: Dorward D.A. et al.
**摘要**: 通过流式细胞术和免疫荧光验证了FPR3抗体在树突状细胞中的特异性表达,发现FPR3激活可增强抗原呈递能力,提示其在适应性免疫应答中的调控作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *FPR3 regulates EGFR-mediated Akt signaling and tumor growth in triple-negative breast cancer*
**作者**: Li Y. et al.
**摘要**: 利用FPR3中和抗体阻断受体功能,发现其显著抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞的Akt磷酸化和体内肿瘤生长,揭示了FPR3通过EGFR信号通路促进癌症进展的机制。
---
**备注**:以上信息为基于领域知识的概括性描述,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如"FPR3 antibody")获取。
FPR3 (Formyl Peptide Receptor 3) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) belonging to the formyl peptide receptor family, which includes FPR1. FPR2. and FPR3. Initially identified for its role in detecting pathogen-derived formylated peptides, FPR3 is primarily expressed in immune cells, such as neutrophils, monocytes, and dendritic cells. Unlike FPR1 and FPR2. which exhibit broad ligand specificity and pro-inflammatory functions, FPR3 has distinct ligand preferences and is implicated in both pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory responses. It binds various ligands, including annexin A1-derived peptides, lipoxin A4. and synthetic compounds, activating signaling pathways like MAPK and PI3K-Akt to modulate chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and cytokine release.
Research highlights FPR3's dual role in immune regulation. While it contributes to resolving inflammation by promoting tissue repair and suppressing excessive immune activation, aberrant FPR3 expression is linked to diseases such as cancer, sepsis, and autoimmune disorders. Antibodies targeting FPR3 are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional mechanisms. They enable applications like immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blotting, aiding in understanding FPR3's involvement in disease pathways. Recent studies also explore therapeutic potential, with FPR3 antibodies investigated for modulating immune responses in chronic inflammation or enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Despite progress, FPR3's precise physiological and pathological roles remain under investigation, necessitating further research to clarify its therapeutic targeting prospects.
×