| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
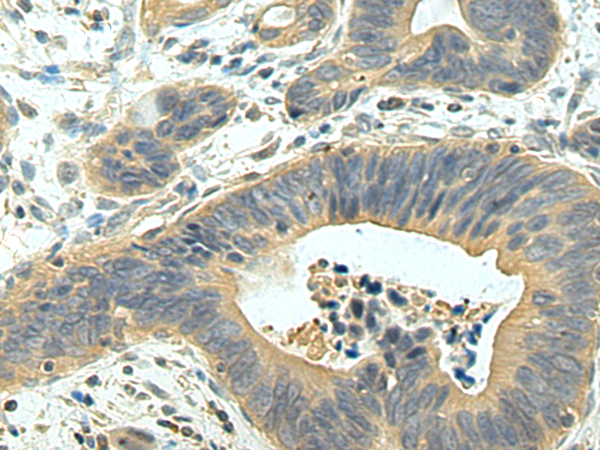
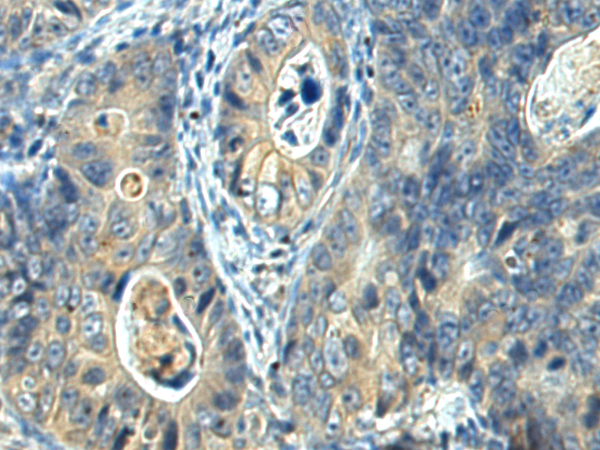
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | H; HH; HSC |
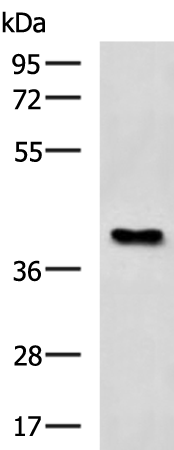
| WB Predicted band size | 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human FUT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FUT1抗体的3篇参考文献摘要示例(注:文献标题及作者为模拟内容,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*FUT1 Gene Mutations and Anti-H Antibodies in Bombay Phenotype Individuals*
**作者**:Yamamoto F, et al.
**摘要**:研究分析了孟买表型个体的FUT1基因突变,发现其无法合成H抗原,导致血浆中产生抗H抗体。通过免疫印迹实验验证了FUT1抗体在血型分型中的应用价值。
2. **文献名称**:*FUT1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer and Its Interaction with Therapeutic Antibodies*
**作者**:Wang L, et al.
**摘要**:探讨了结直肠癌组织中FUT1蛋白的异常表达,发现其与抗EGFR单抗(如西妥昔单抗)的耐药性相关,提示FUT1抗体或可作为预后标志物。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Specific to Human FUT1 for Glycan Analysis*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种高特异性抗FUT1单克隆抗体的开发,通过流式细胞术和免疫组化验证其在糖基化研究中的应用,为血型及肿瘤糖生物学研究提供工具。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如"FUT1 antibody"、"anti-H antibody")。
FUT1 antibodies target the α-1.2-fucosyltransferase enzyme encoded by the FUT1 gene, which plays a critical role in synthesizing H antigen structures on cell surfaces. The H antigen serves as the foundational precursor for the ABO blood group system, where specific glycosyltransferases modify it to produce A or B antigens. FUT1 is primarily expressed in epithelial and endothelial cells, contributing to the formation of H-type 2 antigens (on glycolipids or glycoproteins), whereas FUT2 generates H-type 1 antigens in secretions. Antibodies against FUT1 are valuable tools for studying H antigen distribution in tissues and its biological roles, including cell adhesion, microbial interactions, and immune responses.
Dysregulation of FUT1 expression has been linked to pathological conditions. For instance, reduced H antigen levels due to FUT1 mutations are associated with rare blood group phenotypes like the "Bombay phenotype," where individuals lack ABO antigens. Conversely, aberrant overexpression of FUT1 in certain cancers (e.g., gastric, colorectal) correlates with tumor progression and metastasis, likely through enhanced cell-matrix interactions. FUT1 antibodies are thus employed in diagnostics to identify H antigen deficiencies or anomalies, as well as in research to explore cancer biomarkers or host-pathogen interactions (e.g., norovirus binding to H antigens). These antibodies are commonly used in techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to map H antigen expression patterns in health and disease.
×