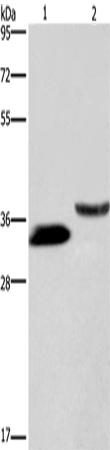
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
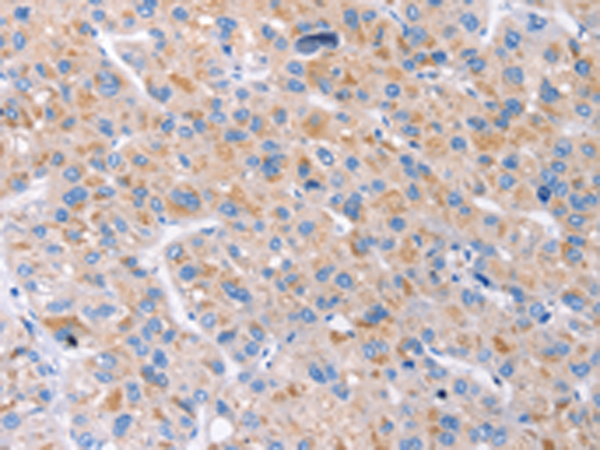
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 36 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GAS1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GAS1抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **标题**: *GAS1 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma via the Hedgehog signaling pathway*
**作者**: Martinelli, R. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过Western blot和免疫组化实验,使用GAS1抗体检测肝癌细胞中GAS1蛋白的表达。结果表明,GAS1通过抑制Hedgehog通路抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并促进凋亡,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **标题**: *Growth Arrest-Specific 1 (GAS1) is a Critical Regulator of Neural Stem Cell Differentiation*
**作者**: Schneider, S. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用GAS1抗体进行免疫荧光染色,发现GAS1在小鼠神经干细胞中高表达,并通过调控Retinoic Acid信号通路促进分化,为神经发育机制提供了新见解。
---
3. **标题**: *GAS1 interacts with PTCH1 to regulate Sonic Hedgehog signaling in development*
**作者**: Allen, B.L. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和免疫印迹实验,验证GAS1与PTCH1的相互作用。研究揭示GAS1作为Hedgehog信号通路的共受体,影响胚胎发育过程中的细胞命运决定。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对准确标题及作者。若需具体文献,可进一步提供研究方向(如疾病模型、实验技术等)。
The Growth Arrest-Specific 1 (GAS1) protein is a cell membrane-associated molecule initially identified in fibroblasts during growth arrest. It plays a critical role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, primarily by modulating key signaling pathways such as Hedgehog (Hh) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) signaling. GAS1 acts as a co-receptor, enhancing Hh pathway activity by binding to the receptor Patched-1 (PTCH1), while paradoxically inhibiting GDNF signaling by interfering with the RET receptor tyrosine kinase. Its dual regulatory function makes it pivotal in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and cancer progression.
GAS1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying the expression, localization, and functional roles of GAS1 in both physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate GAS1's involvement in neurodevelopment, organogenesis, and diseases such as cancer, where its expression is often dysregulated. Research has also explored GAS1's potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in tumors reliant on Hh or GDNF signaling. However, its context-dependent roles—acting as either a tumor suppressor or promoter—highlight the need for precise characterization using specific antibodies to unravel its complex biological mechanisms.
×