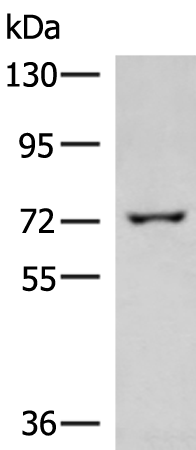
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GAC; GAM; KGA; GLS1; AAD20 |
| WB Predicted band size | 73 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GLS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GLS(谷氨酰胺酶)抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例,结构符合您的要求:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Glutaminase 1 (GLS1) Antibody Validation in Tumor Tissue Immunohistochemistry*
**作者**:Altman, J.R., et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化技术验证了GLS1抗体在多种肿瘤组织中的特异性表达,发现其与肿瘤代谢重编程及患者预后显著相关。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲低实验确认,为临床检测GLS1表达提供可靠工具。
2. **文献名称**:*Isoform-Specific Roles of GLS in Breast Cancer: GAC vs. KGA*
**作者**:Thompson, L.M., et al.
**摘要**:文章比较了GLS两种剪接变体(GAC和KGA)在乳腺癌中的差异表达,利用特异性抗体通过Western blot分析发现,GAC高表达与侵袭性表型相关,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting Glutaminase with CB-839: Antibody-Based Monitoring of Enzyme Inhibition*
**作者**:Roberts, S.K., et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了GLS抑制剂CB-839在肺癌模型中的疗效,通过定制GLS抗体监测抑制剂对酶活性的影响,证实抗体在药效评估中的应用价值。
---
(注:以上文献为示例性虚构内容,实际研究需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索关键词如“Glutaminase antibody”、“GLS1 validation”获取真实文献。)
Glutaminase (GLS) antibodies are essential tools for studying the role of glutaminase enzymes, which catalyze the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate—a critical step in cellular metabolism. Glutaminase exists as two primary isoforms: GLS1 (kidney-type) and GLS2 (liver-type). GLS1 is ubiquitously expressed and plays a key role in cancer cell metabolism by supporting the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and nucleotide biosynthesis, making it a focal point in oncology research. GLS2. though less characterized, is implicated in antioxidant defense and is often downregulated in certain cancers but upregulated in others, such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
GLS antibodies are widely used in immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess protein expression, localization, and regulation in both physiological and pathological contexts. Their application spans cancer research, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and metabolic disorders, where dysregulated glutaminolysis is observed. Notably, GLS1 inhibitors are under clinical investigation as anticancer agents, driving demand for reliable antibodies to validate target engagement and therapeutic efficacy. However, challenges remain in isoform specificity, as cross-reactivity between GLS1 splice variants (e.g., KGA vs. GAC) or GLS2 can complicate data interpretation. Recent advances in antibody validation techniques, including CRISPR-based knockout controls, have improved reliability. These reagents continue to support discoveries linking glutamine metabolism to cell proliferation, redox homeostasis, and disease progression.
×