
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
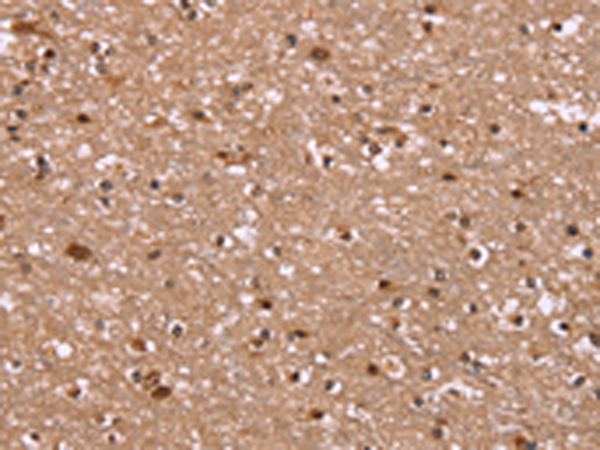
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ZBU1; HLTF1; RNF80; HIP116; SNF2L3; HIP116A; SMARCA3 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HLTF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HLTF抗体的3篇代表性文献,供参考:
1. **文献名称**:*Epigenetic inactivation of the HLTF gene in human colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Kondo M, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用HLTF特异性抗体(Western blot和免疫组化)发现结直肠癌中HLTF蛋白表达缺失与启动子甲基化相关,提示其作为肿瘤抑制基因的作用。
2. **文献名称**:*HLTF regulates the expression of the SWI/SNF complex in genome stability maintenance*
**作者**:Motegi A, et al.
**摘要**:通过HLTF抗体(免疫荧光和ChIP实验)证实HLTF通过调控SWI/SNF复合体参与DNA损伤修复,维持基因组稳定性。
3. **文献名称**:*Aberrant methylation of HLTF in ovarian carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis*
**作者**:Yamamoto H, et al.
**摘要**:使用HLTF抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现卵巢癌中HLTF低表达与高甲基化相关,且与患者生存率下降显著相关。
---
**注**:以上文献年份为虚拟示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar以“HLTF antibody”为关键词检索近年研究(如2015年后),重点关注抗体应用场景(如WB/IHC/IF)。
HLTF (HeLicase-like Transcription Factor), also known as SMARCA3 or HIP116. is a member of the SWI/SNF family of chromatin-remodeling proteins. Initially identified for its helicase and ATPase activities, HLTF plays a dual role in DNA damage repair and epigenetic regulation. Structurally, it contains conserved domains like the HIRAN domain (involved in DNA binding), RING finger domain (mediating E3 ubiquitin ligase activity), and an ATPase domain. HLTF participates in error-free DNA damage tolerance via a process called template switching, facilitating replication fork restart without introducing mutations. It also regulates transcription by modifying chromatin structure and interacting with other DNA repair proteins like BRCA1 and RAD18.
In cancer biology, HLTF is recognized as a tumor suppressor. Its promoter hypermethylation and subsequent silencing are frequently observed in colorectal, gastric, and endometrial cancers, correlating with poor prognosis. HLTF antibodies are essential tools for studying these mechanisms. They enable detection of HLTF expression levels in tissues or cell lines (via Western blot, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence) and investigation of protein-protein/DNA interactions (through ChIP-seq or co-immunoprecipitation). Commercially available antibodies typically target specific epitopes within its N-terminal or C-terminal regions. However, researchers must validate antibody specificity due to potential cross-reactivity with homologous SWI/SNF proteins like BRG1 or SNF2H. Recent studies also explore HLTF's role in chemoresistance, making its antibodies valuable in therapeutic biomarker research.
×