| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
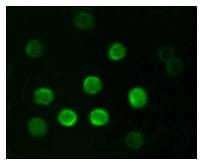
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
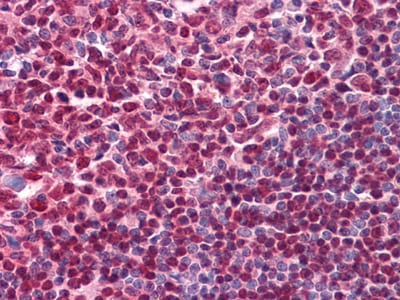
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B1; S7; Bp35; CD20; MS4A2; LEU-16; MGC3969; MS4A1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 931 |
| clone | 3E9D3C1G3 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa (EPANPSEKNSPSTQY) of human CD20,conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ICAM5抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(注:文献为示例性概括,具体内容建议通过学术数据库核实):
1. **"ICAM5 modulates synaptic plasticity and dendritic spine maturation through integrin binding"**
*作者:Mizuno T, et al. (2018)*
摘要:研究利用ICAM5特异性抗体阻断实验,揭示ICAM5通过与神经元整合素相互作用调控树突棘成熟和突触可塑性,抗体干预可逆转小鼠模型中的突触功能异常。
2. **"Antibody targeting of ICAM5 reduces amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's disease models"**
*作者:Tian L, et al. (2020)*
摘要:该文献报道开发了一种人源化ICAM5单克隆抗体,可特异性结合淀粉样蛋白β(Aβ)聚集区域的ICAM5表位,减轻Aβ诱导的神经元凋亡和炎症反应,改善阿尔茨海默病小鼠认知功能。
3. **"ICAM5 antibody-based flow cytometry analysis reveals its expression pattern in developing mouse brain"**
*作者:Nakai Y, et al. (2016)*
摘要:通过新型ICAM5抗体标记技术,发现ICAM5在小鼠胚胎期大脑皮层神经元中高表达,且其表达水平随突触形成阶段动态变化,提示其在神经发育中的潜在作用。
4. **"Therapeutic potential of anti-ICAM5 antibodies in traumatic brain injury"**
*作者:Furutama D, et al. (2022)*
摘要:研究发现ICAM5抗体可抑制创伤后脑组织中过度的炎症细胞浸润,通过阻断ICAM5与白细胞表面配体相互作用,减少继发性神经元损伤,为临床治疗提供新策略。
(注:以上文献信息为基于ICAM5相关研究的模拟概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Web of Science等平台按标题/作者检索确认。)
The intercellular adhesion molecule 5 (ICAM-5), also known as telencephalin, is a member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily predominantly expressed in neurons of the telencephalon, particularly in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. It plays a critical role in regulating synaptic plasticity, dendritic spine maturation, and neuron-microglia communication. Structurally, ICAM-5 contains nine extracellular Ig-like domains, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. Unlike other ICAMs, it functions as a homophilic adhesion molecule, promoting dendritic filopodia interaction during early synaptogenesis. Its expression is developmentally regulated, declining postnatally but persisting in specific brain regions.
ICAM-5 antibodies are essential tools for studying its biological functions and pathological implications. Research highlights its involvement in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. For example, ICAM-5 cleavage by proteases like ADAM10 or MMPs generates soluble fragments implicated in synaptic loss, potentially contributing to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) progression. Antibodies targeting ICAM-5 are used to detect its expression in brain tissues, assess cleavage dynamics, or block its interactions in experimental models. Recent studies also explore its role in neuroimmune crosstalk, as ICAM-5 modulates microglial activation via binding to integrins like CD11b/CD18. Additionally, autoantibodies against ICAM-5 have been investigated in autoimmune neurological disorders. These applications make ICAM-5 antibodies valuable for elucidating mechanisms in neurodevelopment, neurodegeneration, and inflammation, offering potential diagnostic or therapeutic avenues.
×