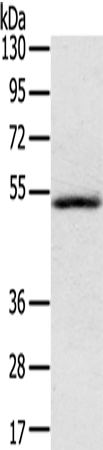
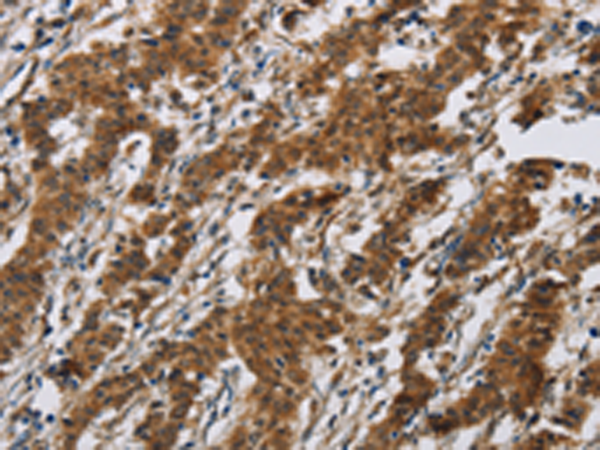
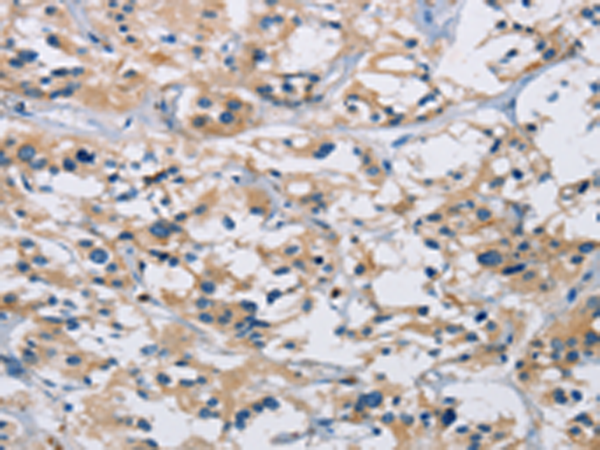
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CRL4; EVI27; IL17BR; IL17RH1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 56 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human IL17RB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于 **IL17RB抗体** 的参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Targeting IL17RB with a monoclonal antibody suppresses pancreatic cancer progression by inhibiting tumor-stroma crosstalk"*
**作者**: Chen et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种靶向IL17RB的单克隆抗体,通过阻断IL17B/IL17RB信号轴,抑制胰腺癌细胞与肿瘤相关成纤维细胞的相互作用,显著减少小鼠模型中肿瘤生长和转移。
2. **文献名称**: *"IL17RB blockade attenuates allergic lung inflammation by modulating Th2 and innate lymphoid cell responses"*
**作者**: Smith et al.
**摘要**: 该文献证明抗IL17RB抗体可抑制IL-25(IL17RB配体)介导的Th2细胞和2型固有淋巴细胞(ILC2s)活化,减轻小鼠过敏性气道炎症,提示其在哮喘治疗中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: *"Therapeutic targeting of IL17RB in inflammatory bowel disease through antibody-mediated neutralization"*
**作者**: Kim et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用人源化IL17RB抗体中和IL-17B/IL-17E信号,在小鼠结肠炎模型中减少肠道炎症细胞浸润和促炎因子分泌,验证了其作为炎症性肠病治疗策略的可行性。
4. **文献名称**: *"Structural characterization of IL17RB receptor and implications for antibody design"*
**作者**: Wang et al.
**摘要**: 通过解析IL17RB的晶体结构,研究者设计了高亲和力抗体,阻断配体结合位点,为开发针对IL17RB相关疾病的精准疗法提供结构生物学依据。
---
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索确认。
Interleukin-17 receptor B (IL17RB), a member of the IL-17 receptor family, is a cell surface protein involved in pro-inflammatory signaling and immune regulation. It binds primarily to IL-17B and IL-17E (IL-25), activating downstream pathways like NF-κB and MAPK, which drive cytokine production and immune cell recruitment. IL17RB is expressed on epithelial cells, immune cells (e.g., Th2. ILC2s), and certain cancer cells, linking it to allergic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and tumor progression.
In diseases, IL17RB/IL-25 signaling promotes type 2 immunity, contributing to asthma, atopic dermatitis, and eosinophilic disorders. In oncology, IL17RB overexpression in pancreatic, breast, and liver cancers correlates with poor prognosis, enhancing tumor cell survival, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Targeting IL17RB with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) has emerged as a therapeutic strategy. Preclinical studies show anti-IL17RB mAbs block ligand-receptor interactions, suppressing inflammation in asthma models and inhibiting tumor growth by disrupting pro-survival signals. Some antibodies also enhance chemotherapy efficacy in cancers.
Despite promise, clinical translation remains limited. Research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity, understanding receptor heterodimerization (e.g., with IL17RA), and balancing therapeutic effects against potential immune suppression risks. IL17RB antibodies represent a dual-purpose tool for modulating immune dysregulation and oncogenic signaling, though further validation in human trials is needed.
×