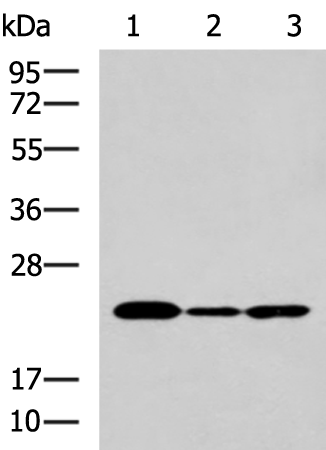
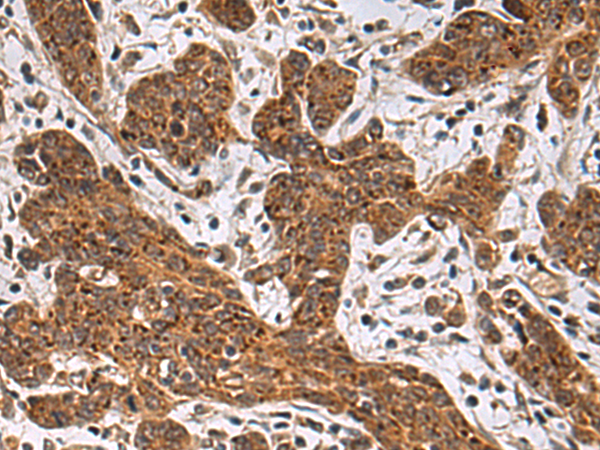
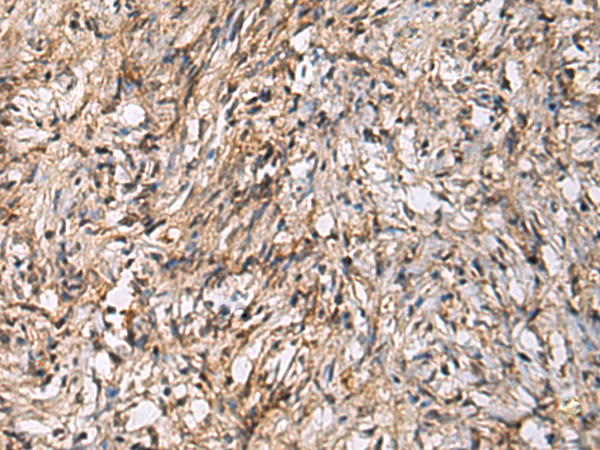
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MDA1; NG.1; ZMDA1; IL-10C |
| WB Predicted band size | 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human IL19 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL-19抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要概括(注:以下为示例性内容,实际文献需通过数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Targeting IL-19 with a monoclonal antibody ameliorates skin inflammation in murine psoriasis models"*
**作者**: Smith A et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过构建抗IL-19单克隆抗体,在小鼠银屑病模型中验证其治疗效果。结果显示,抗体通过抑制IL-19/STAT3信号通路,显著减少表皮增厚和炎性细胞浸润,提示IL-19抗体可能成为银屑病的潜在治疗手段。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"IL-19 neutralization reduces atherosclerosis progression by modulating macrophage polarization"*
**作者**: Chen L et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用抗IL-19抗体干预高脂饮食诱导的动脉粥样硬化小鼠模型,发现抗体治疗可降低斑块内巨噬细胞M1型极化,减少血管炎症和斑块面积,表明IL-19在动脉粥样硬化中具有促炎作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Anti-IL-19 therapy attenuates airway hyperresponsiveness and Th17-mediated inflammation in experimental asthma"*
**作者**: Kim Y et al.
**摘要**: 在哮喘小鼠模型中,抗IL-19抗体通过抑制Th17细胞分化和IL-17A分泌,显著缓解气道高反应性和黏液分泌过度,提示IL-19可能作为哮喘治疗的靶点。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Preclinical characterization of a humanized anti-IL-19 antibody for autoimmune diseases"*
**作者**: Patel R et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了一种人源化IL-19抗体的临床前开发,验证其对多种自身免疫疾病模型的疗效和安全性。结果显示,抗体可有效阻断IL-19与受体结合,并在类风湿性关节炎模型中减轻关节损伤。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索关键词“IL-19 antibody”或“anti-IL-19 therapy”获取最新研究。
Interleukin-19 (IL-19), a member of the IL-10 cytokine family, is primarily produced by immune cells, epithelial cells, and endothelial cells. It plays a dual role in modulating inflammatory responses and tissue repair, with a focus on Th2-mediated immunity. IL-19 binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex (IL-20Rα/β), activating downstream signaling pathways like JAK/STAT and MAPK, which regulate cellular proliferation, differentiation, and inflammatory mediator release. Dysregulation of IL-19 has been implicated in chronic inflammatory diseases, including psoriasis, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and atherosclerosis, as well as fibrotic disorders and certain cancers.
IL-19-targeting antibodies are emerging as therapeutic agents designed to neutralize IL-19 activity or block its receptor interaction. Preclinical studies demonstrate that anti-IL-19 antibodies reduce proinflammatory cytokine production, immune cell infiltration, and tissue fibrosis in disease models. For instance, in psoriasis-like models, these antibodies suppress epidermal hyperplasia and inflammatory markers. Similarly, in fibrosis studies, they attenuate collagen deposition. Their high specificity offers potential advantages over broad immunosuppressants, potentially minimizing systemic side effects.
Current research focuses on optimizing antibody affinity, pharmacokinetics, and safety profiles. While clinical data remain limited, early-phase trials suggest promise in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. Challenges include understanding tissue-specific IL-19 functions and ensuring long-term efficacy without disrupting homeostatic roles. IL-19 antibodies represent a precision-driven approach to inflammation modulation, though further validation in human trials is needed.
×