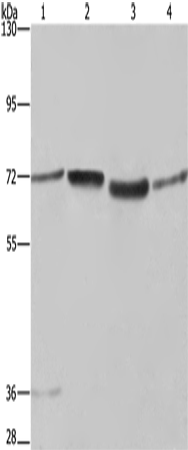
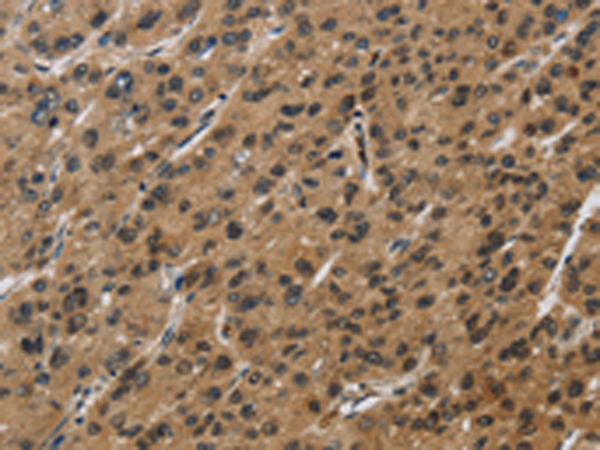
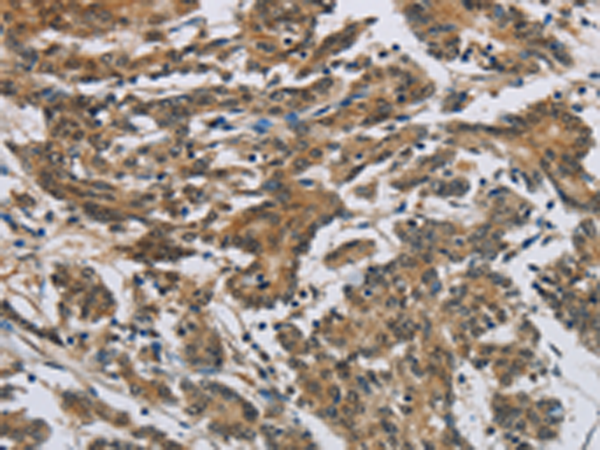
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SYNI; SYN1a; SYN1b |
| WB Predicted band size | 74 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SYN1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SYN1(Synapsin 1)抗体的3篇参考文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**: "Synapsin I: a major synaptic phosphoprotein associated with small synaptic vesicles"
**作者**: De Camilli, P., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用SYN1抗体鉴定了Synapsin I在大鼠脑组织中的定位,发现其富集于突触小泡膜表面,并参与调控神经递质释放。抗体染色显示其与神经元突触前终末的特异性结合。
2. **文献名称**: "Altered expression of synapsin I in temporal lobe epilepsy"
**作者**: Ketzef, M., et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化结合SYN1抗体,研究发现颞叶癫痫患者海马区Synapsin I表达显著下降,提示突触囊泡运输异常可能与癫痫发病机制相关。
3. **文献名称**: "Synapsin I deficiency delays hippocampal development and enhances environmental stimulation"
**作者**: Gitler, D., et al.
**摘要**: 利用SYN1抗体对基因敲除小鼠脑组织分析,发现Synapsin I缺失导致海马突触成熟延迟,但环境刺激可部分代偿其功能,表明该蛋白在突触可塑性中的关键作用。
4. **文献名称**: "Activity-dependent phosphorylation of synapsin I by CaMKII regulates synaptic vesicle clustering"
**作者**: Jovanovic, J.N., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过磷酸化特异性SYN1抗体证实,钙调蛋白激酶II(CaMKII)介导的Synapsin I磷酸化可调节突触小泡的聚集与释放效率,揭示其动态调控机制。
(注:以上文献标题和作者为示例性总结,具体内容需根据实际发表文献调整。)
The Synapsin 1 (SYN1) antibody is a key tool in neuroscience research, targeting the SYN1 protein—a member of the synapsin family critical for regulating synaptic vesicle dynamics. Synapsins are phosphoproteins primarily localized to presynaptic terminals, where they tether synaptic vesicles to the cytoskeleton, modulating neurotransmitter release in response to neuronal activity. SYN1. encoded by the SYN1 gene, plays a role in synapse formation, plasticity, and maintenance.
SYN1 antibodies are widely used to study synaptic architecture and function in both normal and pathological contexts. They enable visualization of presynaptic compartments via techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF), and quantify protein expression through Western blotting. Dysregulation of SYN1 has been linked to neurological disorders, including epilepsy, autism spectrum disorders, and schizophrenia, making these antibodies valuable for investigating disease mechanisms.
First developed in the 1980s, SYN1 antibodies have evolved with advances in specificity and sensitivity, often generated in hosts like rabbits or mice using recombinant protein fragments. Their applications extend to developmental studies, exploring synaptic maturation, and drug research targeting synaptic dysfunction. By elucidating SYN1's role in neuronal communication, these antibodies remain pivotal in unraveling brain complexity and disease pathways.
×