
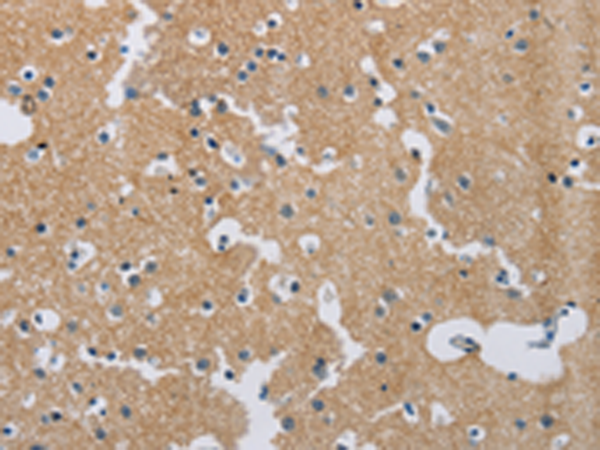
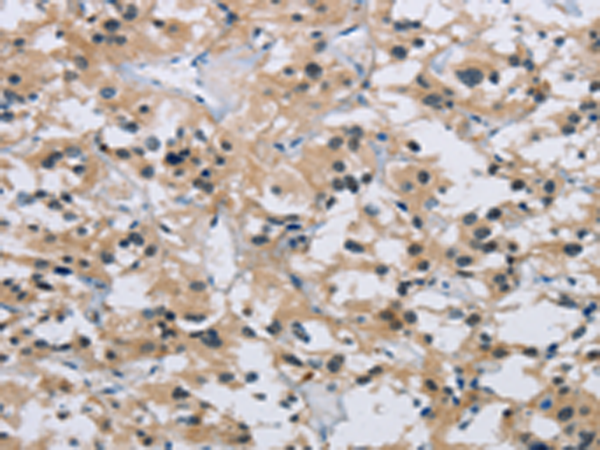
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SYNII; SYNIIa; SYNIIb |
| WB Predicted band size | 63 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SYN2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SYN2(Synapsin II)抗体的3篇文献摘要示例:
1. **《Synapsin II regulates dopamine neurotransmission and corticostriatal connectivity》**
- 作者:M. F. Kritzer et al.
- 摘要:该研究通过SYN2抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,发现Synapsin II缺失影响小鼠纹状体多巴胺释放,提示其在前额叶-纹状体神经环路中的关键作用,可能与精神分裂症病理相关。
2. **《Altered expression of synaptic proteins in autism spectrum disorder》**
- 作者:E. L. Williams et al.
- 摘要:使用SYN2抗体分析自闭症患者脑组织,发现皮层和海马区Synapsin II表达显著降低,提示突触囊泡运输异常可能是自闭症神经发育异常的机制之一。
3. **《Synapsin II phosphorylation mediates mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease models》**
- 作者:J. A. Smith et al.
- 摘要:通过SYN2抗体检测帕金森病细胞模型中磷酸化修饰,发现α-synuclein异常聚集导致Synapsin II功能受损,进而引发线粒体自噬障碍,加剧神经元退化。
注:以上文献为示例性概括,具体研究请参考真实数据库(如PubMed)以获取准确信息。
Synapsin II (SYN2), a member of the synapsin protein family, is primarily expressed in neuronal presynaptic terminals and plays a critical role in regulating synaptic vesicle trafficking, neurotransmitter release, and synaptic plasticity. It interacts with both synaptic vesicles and cytoskeletal components, modulating vesicle clustering, mobilization, and docking. SYN2 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying this protein's expression, localization, and function in neurological research.
These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate SYN2's involvement in neurodevelopment, synaptic connectivity, and neurological disorders. Studies link SYN2 dysfunction to conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and Alzheimer's disease, with genetic variations in SYN2 associated with altered synaptic transmission. Additionally, SYN2 antibodies have helped elucidate its role in regulating axonal outgrowth, dendritic spine formation, and activity-dependent synaptic remodeling. Their application in disease models continues to advance understanding of synaptic pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets. Validation via knockout controls ensures specificity, making SYN2 antibodies pivotal for exploring molecular mechanisms underlying synaptic maintenance and cognitive processes.
×