| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
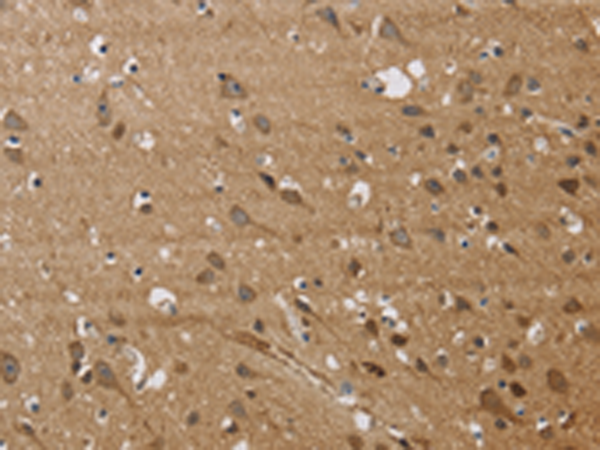
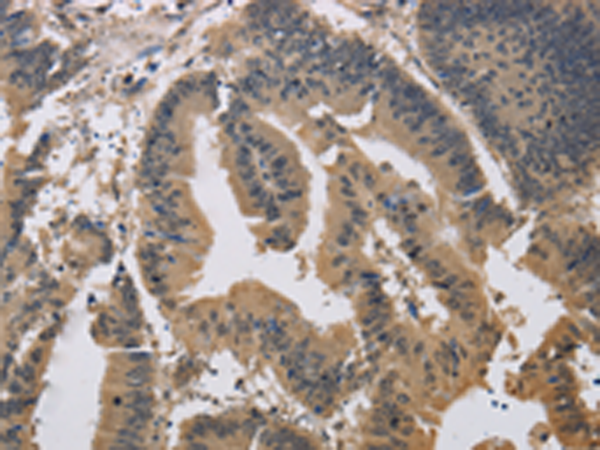
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AGS; AHD; AWS; HJ1; CD339; JAGL1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human JAG1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于JAG1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的简要总结:
1. **文献名称**: "Jagged1 Antibody Therapy Inhibits Tumor Growth in Colorectal Cancer by Targeting Notch Signaling"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种特异性JAG1抗体通过阻断Notch信号通路,抑制结直肠癌肿瘤细胞的增殖和转移,在体内外实验中均显示出显著的抗肿瘤活性。
2. **文献名称**: "JAG1/Notch1 Signaling as a Prognostic Marker in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献发现JAG1蛋白在三阴性乳腺癌组织中高表达,并与其不良预后相关。使用JAG1抗体进行免疫组化分析,证实其可作为潜在预后标志物和治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**: "Anti-JAG1 Antibody Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis via Modulating Alveolar Epithelial Cell Senescence"
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用JAG1抗体干预肺纤维化模型,发现其通过抑制肺泡上皮细胞衰老和减少细胞外基质沉积,显著减缓纤维化进程,为治疗肺纤维化提供了新策略。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性内容,实际引用需核对真实数据库如PubMed或Google Scholar中的具体文献。)
The JAG1 antibody is designed to target the Jagged-1 (JAG1) protein, a critical ligand in the evolutionarily conserved Notch signaling pathway. JAG1 is a transmembrane protein predominantly expressed on the cell surface, playing a pivotal role in cell-cell communication, differentiation, proliferation, and tissue development. Structurally, it contains a large extracellular domain with multiple epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats and a DSL (Delta/Serrate/Lag-2) domain essential for binding to Notch receptors. Dysregulation of JAG1-mediated Notch signaling has been implicated in various pathologies, including cancers (e.g., breast, liver, leukemia), cardiovascular disorders, and developmental syndromes like Alagille syndrome (caused by JAG1 gene mutations).
JAG1 antibodies are widely utilized in research to detect JAG1 expression levels in tissues or cell lines via techniques such as immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, or flow cytometry. They also serve as tools to modulate Notch signaling in experimental settings, either by blocking ligand-receptor interactions or activating downstream pathways. Clinically, JAG1 antibodies are being explored as potential therapeutic agents, particularly in oncology, where Notch signaling often drives tumor progression and therapy resistance. However, challenges remain in achieving specificity and minimizing off-target effects due to the pathway's complexity and context-dependent roles. Ongoing studies aim to refine antibody design and evaluate their efficacy in preclinical models.
×