
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
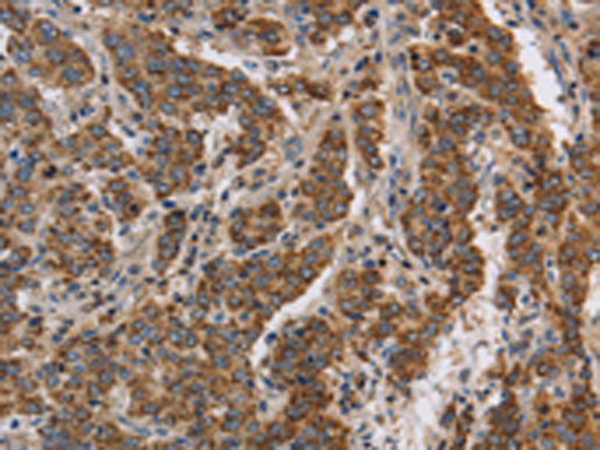
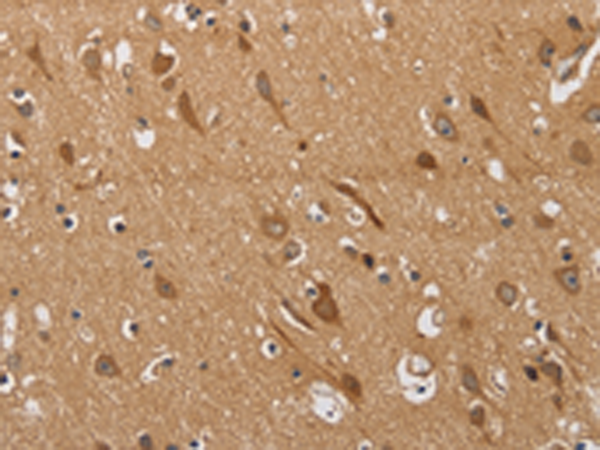
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DFNA2; KV7.4; DFNA2A |
| WB Predicted band size | 77 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human KCNQ4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于KCNQ4抗体的参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*KCNQ4. a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells, is mutated in dominant deafness*
**作者**:Kubisch C, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次发现KCNQ4基因突变与常染色体显性遗传性耳聋(DFNA2型)相关,并利用特异性抗体证实KCNQ4蛋白在外毛细胞中的表达,提示其在听觉信号传导中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Expression of the KCNQ4 potassium channel in the developing mouse cochlea*
**作者**:Beisel KW, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化结合KCNQ4抗体,研究揭示了小鼠耳蜗发育过程中KCNQ4通道的时空表达模式,表明其参与毛细胞成熟及听觉功能的建立。
---
3. **文献名称**:*KCNQ4 channels in the CNS: Unique subcellular distribution and modulation by neuronal activity*
**作者**:Kharkovets T, et al.
**摘要**:利用KCNQ4特异性抗体进行亚细胞定位分析,发现该通道在特定神经元胞体和突触区域的富集,并证明其活性受神经元电活动调控,可能影响神经兴奋性平衡。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Molecular structure and physiological function of chloride channels and potassium channels*
**作者**:Jentsch TJ, et al.
**摘要**:综述中讨论了KCNQ家族(包括KCNQ4)的结构与功能,引用抗体相关实验数据说明KCNQ4在听觉及神经系统疾病中的病理机制。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需根据具体研究内容核对作者、年份及期刊信息。
The KCNQ4 antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the KCNQ4 protein, a voltage-gated potassium channel subunit encoded by the *KCNQ4* gene. As a member of the Kv7 (KCNQ) family, KCNQ4 plays a critical role in regulating neuronal excitability and auditory function. It is predominantly expressed in the central nervous system, cochlear hair cells, and smooth muscle cells, where it contributes to the maintenance of resting membrane potential and signal transduction. Mutations in *KCNQ4* are linked to autosomal dominant hearing loss (DFNA2) and neurological disorders, underscoring its physiological importance.
KCNQ4 antibodies are widely used in biomedical research to investigate the protein’s expression, localization, and functional interactions. They enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to visualize KCNQ4 distribution in tissues or cultured cells. These antibodies also aid in studying channelopathies, drug responses, and molecular mechanisms underlying diseases. For example, researchers employ them to explore how KCNQ4 dysfunction leads to hyperexcitability in neurons or hearing impairment.
Developed in various host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse), KCNQ4 antibodies are validated for specificity and sensitivity, often targeting epitopes in conserved regions like the C-terminus or pore domain. Their applications extend to screening therapeutic compounds targeting Kv7 channels for conditions like epilepsy or neuropathic pain. However, careful validation is essential to avoid cross-reactivity with homologous KCNQ subunits (e.g., KCNQ2. KCNQ3). Overall, KCNQ4 antibodies are indispensable for advancing our understanding of potassium channel biology and related pathologies.
×