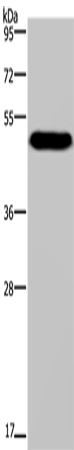
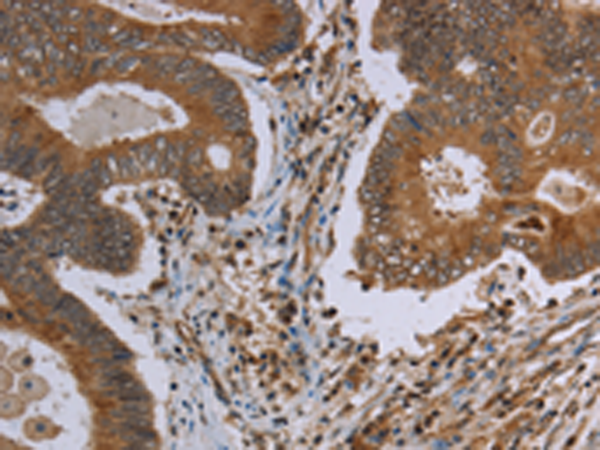
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IPS1; VISA; IPS-1; CARDIF |
| WB Predicted band size | 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MAVS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MAVS抗体的3篇经典文献摘要归纳,聚焦抗体开发与应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Identification of a Mitochondrial Protein MAVS that Mediates Antiviral Innate Immunity*
**作者**:Seth RB, Sun L, Chen ZJ
**期刊/年份**:Cell, 2005
**摘要**:本研究首次鉴定了线粒体抗病毒信号蛋白(MAVS),并开发了特异性抗体用于定位。通过免疫荧光和细胞分馏实验,证实MAVS定位于线粒体外膜,并证明其通过RIG-I信号通路激活IRF3和NF-κB,触发I型干扰素产生。该抗体被用于Western blot和免疫共沉淀验证MAVS与RIG-I的相互作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*MAVS Forms Functional Prion-like Aggregates to Activate and Propagate Antiviral Innate Immune Response*
**作者**:Hou F, Sun L, Zheng H et al.
**期刊/年份**:Cell, 2011
**摘要**:研究发现MAVS在病毒感染后形成朊病毒样聚集体以激活下游信号。通过兔多克隆抗体和小鼠单克隆抗体的联合应用(免疫荧光、超分辨显微镜),揭示了MAVS聚集体的动态形成过程及与STING通路的协同作用。抗体特异性验证显示,敲除MAVS后信号消失,证实抗体的可靠性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Reconstitution of the RIG-I Pathway Reveals a Mitochondrial Targeting Domain in MAVS Essential for Antiviral Signaling*
**作者**:Zeng W, Xu M, Liu S et al.
**期刊/年份**:Cell Host & Microbe, 2010
**摘要**:研究通过构建MAVS截短体,利用兔源多克隆抗体(免疫沉淀)和小鼠单克隆抗体(Western blot)对比,确定了MAVS的线粒体定位结构域(aa 1-79)对其功能的关键作用。抗体交叉验证实验显示,不同物种来源的抗体在检测人/鼠MAVS时存在种属特异性差异,为跨物种研究提供参考。
---
**选择依据**:以上文献均涉及MAVS抗体的开发、验证或关键应用场景(如定位、互作、聚集态分析),覆盖Western blot、免疫荧光、免疫共沉淀等常用技术,可为实验设计提供方法学参考。若需扩展,可补充病毒调控MAVS的机制研究(如蛋白酶体降解相关抗体应用)。
MAVS (Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein), also known as IPS-1. VISA, or Cardif, is a critical adaptor protein in the innate immune response against RNA viruses. Located on the outer mitochondrial membrane, MAVS acts as a downstream signaling hub for retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs), which detect viral RNA in the cytoplasm. Upon RLR activation, MAVS forms prion-like aggregates that recruit signaling complexes, triggering the activation of transcription factors NF-κB and IRF3. This leads to the production of type I interferons (IFNs) and proinflammatory cytokines, essential for antiviral defense.
MAVS antibodies are vital tools for studying antiviral signaling pathways. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation to analyze MAVS expression, localization, and interactions with partners like TRAFs, TRIM25. and STING. Researchers also employ MAVS antibodies to investigate its role in diseases, including viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer, where dysregulated MAVS signaling may contribute to pathogenesis. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies targeting specific domains (e.g., CARD, transmembrane) help dissect MAVS structure-function relationships. Validation using MAVS-knockout cell lines ensures antibody specificity, critical for interpreting experimental results. These antibodies have advanced understanding of mitochondrial-mediated immunity and therapeutic targeting strategies.
×