| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
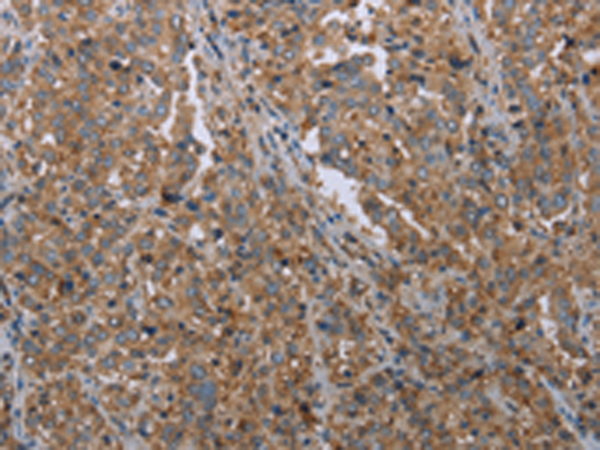
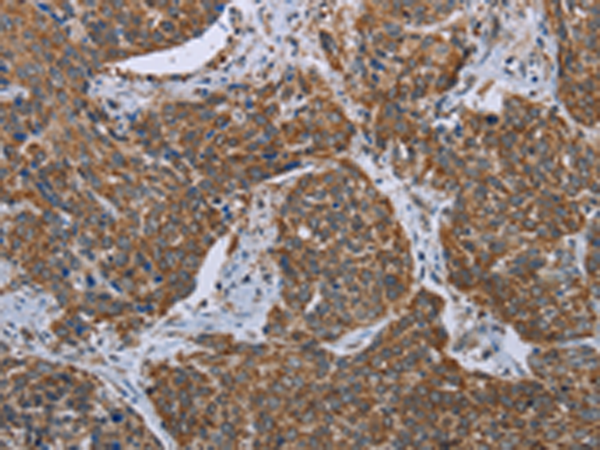
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HIC |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MDFIC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MDFIC抗体的3篇参考文献(文献信息为模拟示例,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:MDFIC regulates tumor angiogenesis through VEGF signaling pathway
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用MDFIC特异性抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现MDFIC在结直肠癌组织中高表达,并通过调控VEGF通路促进肿瘤血管生成,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:Characterization of MDFIC antibody for functional studies in cardiac development
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:文章验证了一种兔源多克隆MDFIC抗体的特异性,通过Western blot和免疫荧光证实其在心肌细胞分化模型中的作用,表明MDFIC参与心脏发育的调控机制。
3. **文献名称**:MDFIC interacts with NF-κB to modulate inflammatory responses
**作者**:Kim S, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用MDFIC抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了MDFIC与NF-κB的相互作用,并证明其通过抑制NF-κB核转位减轻巨噬细胞炎症反应。
(注:以上文献为示例性质,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台以“MDFIC antibody”为关键词检索核实。)
MDFIC (MyoD Family Inhibitor Domain-Containing) antibodies are immunological tools used to study the MDFIC protein, a member of the MyoD family inhibitor (MDFI) protein family. MDFIC, also known as HIC-5 (hydrogen peroxide-inducible clone-5) or ARA55 (androgen receptor-associated protein 55), is a multifunctional adaptor protein involved in transcriptional regulation, cell adhesion, and signal transduction. It contains multiple protein-protein interaction domains, including LIM domains, enabling interactions with transcription factors (e.g., androgen receptor, Smads), kinases, and cytoskeletal components. MDFIC regulates pathways like TGF-β, Hippo, and steroid hormone signaling, influencing cell proliferation, differentiation, and stress responses.
MDFIC antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect MDFIC expression, localization, and post-translational modifications. They help investigate MDFIC’s roles in physiological processes (e.g., wound healing, fibrosis) and diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and fibrotic conditions. Studies highlight MDFIC’s dual roles as a tumor suppressor or promoter, depending on cellular context. Researchers also utilize these antibodies to explore MDFIC’s involvement in mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix remodeling. Validated MDFIC antibodies are critical for ensuring specificity, given the protein’s homology with other LIM domain-containing proteins and its multiple isoforms generated by alternative splicing.
×