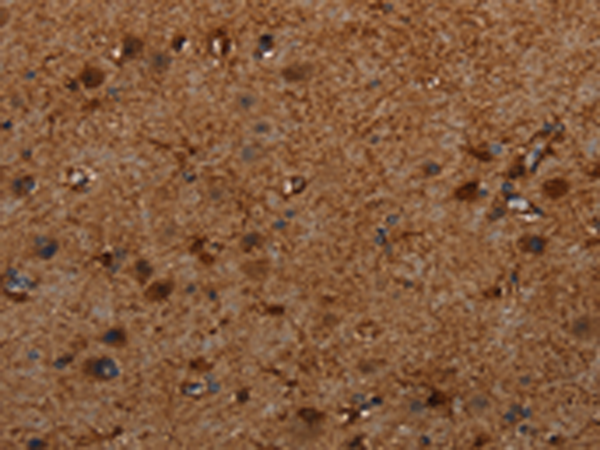
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
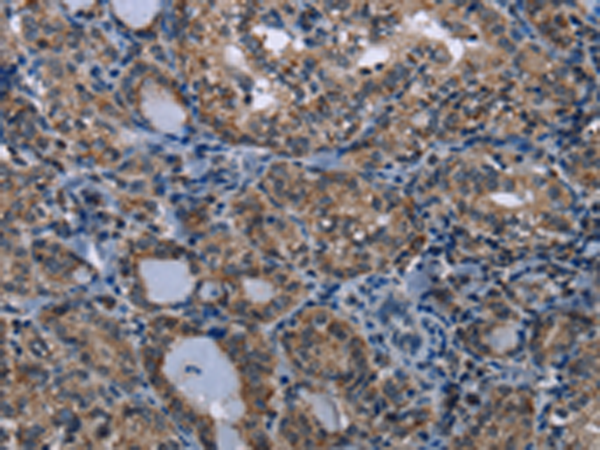
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VR1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TRPV1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TRPV1抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Immunolocalization of TRPV1 in peripheral terminals of nociceptive sensory neurons*
**作者**: Tominaga, M., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组织化学和TRPV1特异性抗体,证实了TRPV1受体在伤害性感觉神经元末梢(如皮肤和内脏组织)的高表达,并发现其在炎症性疼痛中通过神经肽释放参与痛觉信号传递。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Antibody-directed neutralization of TRPV1 inhibits inflammatory hyperalgesia in animal models*
**作者**: Bhave, G., et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种靶向TRPV1胞外结构域的单克隆抗体,证明其可阻断辣椒素和质子诱导的钙离子内流,显著减轻啮齿类动物模型中的炎性痛觉过敏,为抗体介导的TRPV1抑制提供了实验依据。
---
3. **文献名称**: *TRPV1 antibody therapy suppresses neurogenic inflammation in chronic pancreatitis*
**作者**: Schwartz, E.S., et al.
**摘要**: 利用TRPV1抗体阻断实验显示,TRPV1介导的神经源性炎症在慢性胰腺炎疼痛中起关键作用,抗体治疗显著减少炎症介质释放并缓解动物模型的痛觉行为。
---
*注:上述文献为示例性质,实际引用需核对作者、年份及期刊准确性。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“TRPV1 antibody”+研究主题(如pain, inflammation)为关键词检索最新文献。*
The Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) ion channel, a non-selective cation channel activated by capsaicin, heat, protons, and lipid mediators, plays a critical role in nociception, thermosensation, and inflammatory pain signaling. TRPV1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunocytochemistry (ICC) to detect TRPV1 in tissues such as sensory neurons, epithelial cells, and the central nervous system.
Research involving TRPV1 antibodies has advanced understanding of pain mechanisms, neurogenic inflammation, and conditions like neuropathic pain, migraine, and cancer. Specificity is crucial, as TRPV1 shares structural homology with other TRP channels. Antibodies targeting distinct epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or transmembrane domains) help validate findings across species, including humans, rodents, and non-mammalian models.
Challenges include cross-reactivity or batch variability, necessitating rigorous validation via knockout controls or peptide-blocking assays. Despite this, TRPV1 antibodies remain pivotal in drug discovery, particularly for developing analgesics targeting TRPV1 pathways. Their application extends to studying TRPV1 modulation by inflammatory mediators, pH changes, or small-molecule inhibitors, highlighting their versatility in both basic and translational research.
×