
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
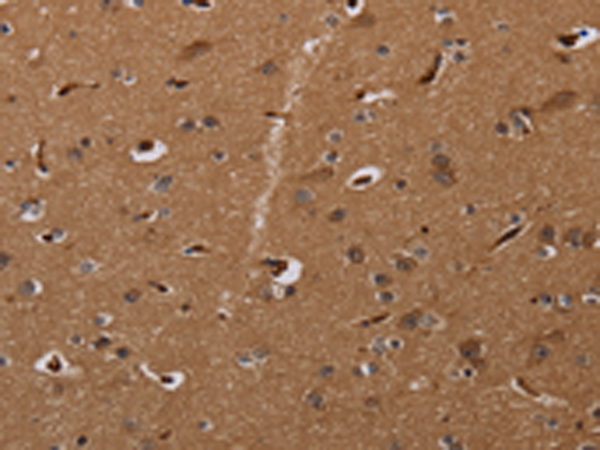
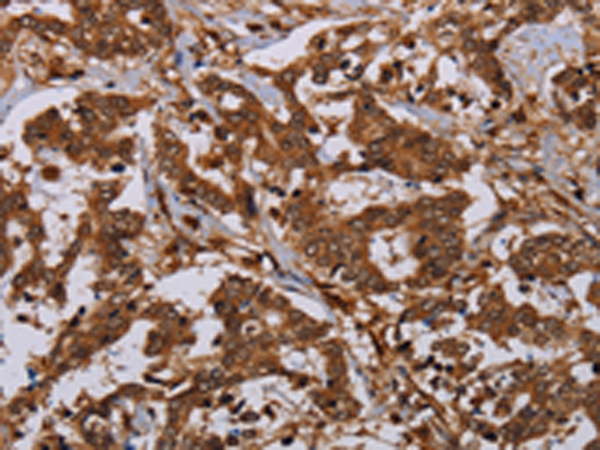
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MOB1; MATS1; Mob4B; C2orf6; MOBK1B; MOBKL1B |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MOB1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于MOB1A抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*MOB1A/B orchestrate Hippo signaling activation through direct binding to LATS kinases*
**作者**:Praskova, M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了MOB1A/B蛋白通过直接结合LATS激酶激活Hippo信号通路,调控细胞增殖和凋亡,并验证了特异性抗体在检测MOB1A磷酸化及相互作用中的应用。
2. **文献名称**:*The MOB1A/B-CST50 complex mediates the DNA damage response in cancer cells*
**作者**:Hergovich, A., et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了MOB1A与CST50的相互作用在DNA损伤修复中的作用,利用MOB1A抗体证实其定位变化及在维持基因组稳定性中的功能。
3. **文献名称**:*MOB1A deficiency promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via YAP1 activation*
**作者**:Xia, H., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(MOB1A抗体)发现,MOB1A低表达与结直肠癌患者预后不良相关,其缺失通过激活YAP1促进肿瘤侵袭转移。
4. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based profiling of MOB1A phosphorylation states in mitotic regulation*
**作者**:Chiyoda, T., et al.
**摘要**:开发了特异性识别磷酸化MOB1A的抗体,证明其在有丝分裂中调控染色体分离和细胞周期进程的关键作用。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究检索PubMed或Google Scholar获取原文信息。)
MOB1A is a key regulatory protein belonging to the MOB (Mps One Binder) superfamily, which plays a critical role in the Hippo signaling pathway. This evolutionarily conserved pathway governs cell proliferation, apoptosis, and organ size by regulating the activity of downstream effectors like YAP/TAZ. MOB1A, along with its homolog MOB1B, acts as a scaffold and co-activator for the serine/threonine kinases LATS1/2. When phosphorylated by upstream kinases (e.g., MST1/2), MOB1A binds to LATS1/2. facilitating their activation and subsequent phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ, leading to their cytoplasmic retention or degradation.
Antibodies targeting MOB1A are essential tools for studying Hippo pathway dynamics. They enable detection of endogenous MOB1A expression, phosphorylation status, and protein-protein interactions in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Such antibodies are widely used in cancer research, as Hippo pathway dysregulation (including MOB1A alterations) is implicated in tumorigenesis, metastasis, and chemoresistance in cancers like breast, liver, and lung carcinomas. Additionally, MOB1A antibodies aid in exploring its non-canonical roles in mitosis, centrosome dynamics, and DNA damage response. Most commercial MOB1A antibodies are raised against specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal regions) and validated for species cross-reactivity (human, mouse, rat). Validation methods often include knockout cell lines to confirm specificity. Researchers prioritize antibodies recognizing both phosphorylated (active) and unphosphorylated MOB1A forms to assess pathway activation status.
×