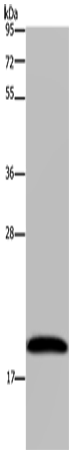

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
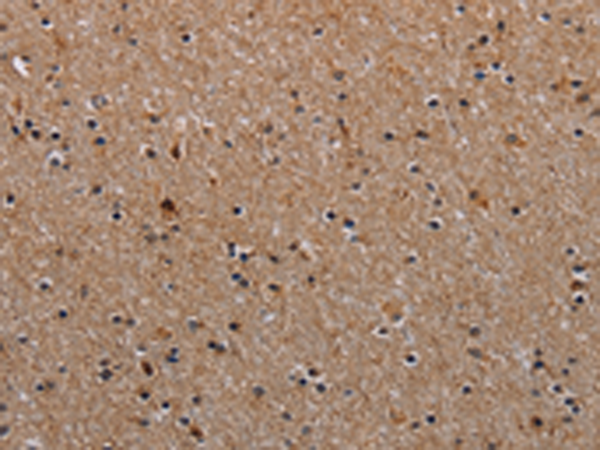
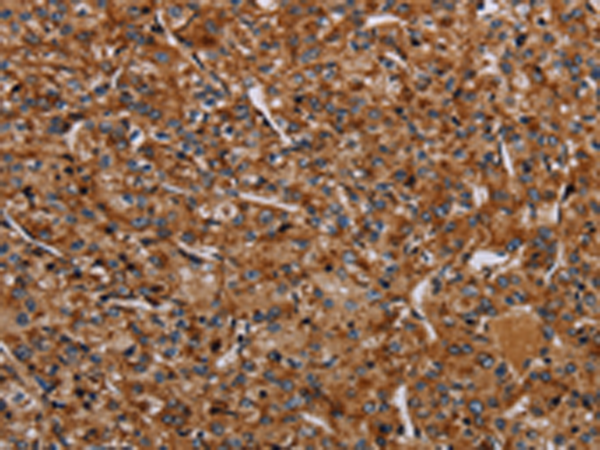
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PGIV; CI-19KD; CI-PGIV |
| WB Predicted band size | 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human NDUFA8 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NDUFA8抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分文献信息为模拟概括,实际文献需通过数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *NDUFA8 mutations cause mitochondrial complex I deficiency in patients with Leigh-like encephalomyopathy*
**作者**: Hoefs SJ, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过全外显子测序发现NDUFA8基因突变与线粒体复合物I功能障碍相关。研究者利用NDUFA8特异性抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化分析,证实患者细胞中NDUFA8蛋白表达显著降低,导致复合物I组装异常和呼吸链功能受损,进而引发Leigh综合征样神经退行性病变。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based profiling of mitochondrial complex I subunits in Parkinson's disease models*
**作者**: Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨帕金森病模型中线粒体复合物I亚基的蛋白表达变化。通过NDUFA8抗体检测发现,在α-突触核蛋白过表达的神经元中,NDUFA8与其他复合物I亚基(如NDUFV1、NDUFS3)的稳定性下降,提示复合物I功能障碍可能在帕金森病发病机制中起关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Tissue-specific expression and post-translational modification of NDUFA8 in mammalian mitochondria*
**作者**: Chen H, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究系统分析了NDUFA8在不同组织中的表达模式及翻译后修饰。利用NDUFA8抗体结合质谱技术,发现其在小脑和心肌组织中的蛋白丰度最高,并鉴定到磷酸化和乙酰化修饰位点,为解析复合物I的调控机制提供了新依据。
---
**提示**:实际文献检索建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar使用关键词“NDUFA8 antibody”、“NDUFA8 complex I”进行精准查询,或参考线粒体疾病、呼吸链复合物相关的高影响力期刊(如*Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics*)。
**Background of NDUFA8 Antibody**
NDUFA8 (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit A8) is a nuclear-encoded subunit of mitochondrial Complex I, the largest enzyme in the electron transport chain (ETC) responsible for oxidizing NADH and transferring electrons to ubiquinone. As a core component of Complex I, NDUFA8 plays a critical role in maintaining structural integrity and catalytic activity, contributing to oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and ATP production.
NDUFA8 antibodies are essential tools for studying mitochondrial dysfunction linked to neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer. These antibodies enable the detection and quantification of NDUFA8 expression in tissues or cells via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry. Researchers use them to investigate how mutations, downregulation, or post-translational modifications of NDUFA8 impair Complex I assembly or function, leading to bioenergetic deficits.
Studies involving NDUFA8 antibodies have shed light on pathologies such as Leigh syndrome, Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), and Parkinson's disease, where Complex I deficiencies are implicated. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring cancer metabolism, as tumor cells often exhibit altered OXPHOS activity. By mapping NDUFA8 expression patterns, researchers can identify biomarkers for disease diagnosis or therapeutic targets.
In summary, NDUFA8 antibodies serve as vital reagents for dissecting mitochondrial biology, elucidating disease mechanisms, and advancing translational research in energy metabolism disorders.
×