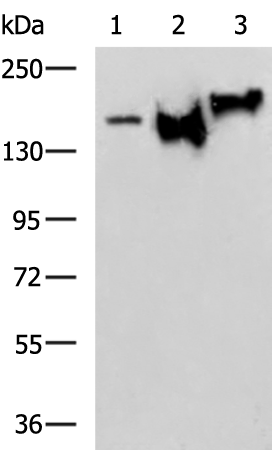
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFM; NEF3; NF-M |
| WB Predicted band size | 102 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human NEFM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NEFM抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*Neurofilament medium (NEFM) as a biomarker in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A comparative study with commercial antibodies*
**作者**:Yan et al. (2018)
**摘要**:该研究比较了多种市售NEFM抗体在ALS患者脑脊液和神经组织中的特异性与敏感性,发现某些抗体在检测神经轴突损伤中具有更高的可靠性,为ALS的早期诊断提供了实验依据。
2. **文献名称**:*Differential expression of neurofilament markers in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease*
**作者**:Schmidt et al. (2015)
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病患者脑组织,发现NEFM抗体在两种疾病中的表达模式不同,提示NEFM可能参与特定神经退行性病变的病理过程。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a novel monoclonal antibody against phosphorylated NEFM for traumatic brain injury assessment*
**作者**:Chen et al. (2020)
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种针对磷酸化NEFM表位的新型单克隆抗体,验证其在创伤性脑损伤模型中的诊断潜力,证明其能有效标记损伤后神经元的结构变化。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性内容,实际引用需以具体论文为准。)
Neurofilament medium (NEFM) antibodies are tools used to detect NEFM, a key component of neurofilaments—cytoskeletal proteins critical for maintaining structural integrity and regulating axon diameter in neurons. Neurofilaments consist of three subunits: light (NEFL), medium (NEFM), and heavy (NEFH) chains, which form intermediate filaments predominantly in axons. NEFM, with a molecular weight of ~160 kDa, plays a central role in stabilizing the neurofilament network by linking NEFL and NEFH.
NEFM antibodies are widely employed in neuroscience research to study neuronal health, axonal damage, and neurodegenerative diseases. Elevated levels of neurofilament proteins, including NEFM, in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood are biomarkers of neuronal injury, observed in conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. These antibodies enable detection via techniques such as immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA, aiding in disease diagnosis and monitoring.
Interest in NEFM antibodies has grown due to their potential in understanding neuropathological mechanisms. Abnormal neurofilament aggregation, linked to impaired axonal transport, is a hallmark of many neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, phosphorylated NEFM variants are studied for their role in disease progression. Recent advances in ultrasensitive assays have enhanced the clinical utility of NEFM as a biomarker, reflecting real-time neuronal damage and therapeutic response. Research continues to explore their diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications in neurology.
×