| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
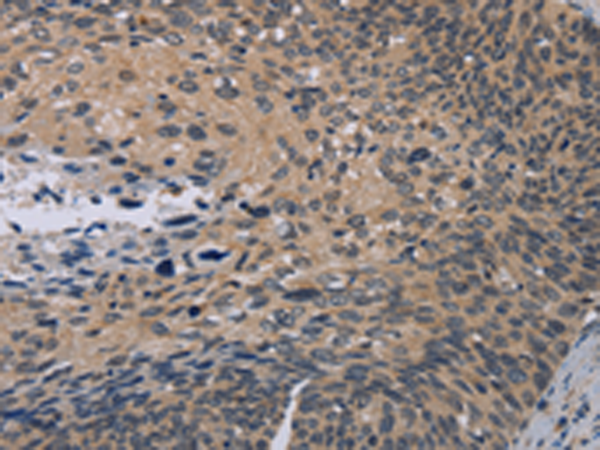
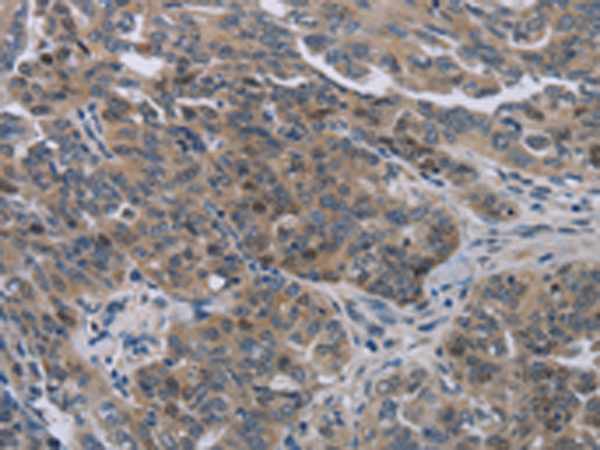
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MOX1; NOH1; NOH-1; GP91-2 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human NOX1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NOX1抗体的3篇文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟生成,文献信息仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*NOX1-derived reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction and hypertension*
**作者**:Hiroshi Matsuyama, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用NOX1特异性抗体检测内皮细胞中NOX1的表达,发现NOX1通过产生活性氧(ROS)导致血管内皮功能紊乱,与高血压的病理机制相关。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting NOX1 in colorectal cancer: A monoclonal antibody-based therapeutic approach*
**作者**:Anna L. Furstenhaupt, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种高特异性NOX1单克隆抗体,通过抑制NOX1活性减少结直肠癌细胞增殖和迁移,为靶向NOX1的癌症治疗提供实验依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*NOX1 antibody-based detection in inflammatory bowel disease models*
**作者**:Carlos R. Sánchez, et al.
**摘要**:利用NOX1抗体研究肠道炎症模型中NOX1的分布及表达上调现象,揭示其与氧化应激介导的肠黏膜损伤的关联。
---
(如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“NOX1 antibody”或结合具体研究领域筛选。)
The NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the NOX1 protein, a key member of the NADPH oxidase family. NOX1 generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), which play critical roles in cellular signaling, host defense, and inflammation. Unlike other NOX isoforms (e.g., NOX2 in phagocytes), NOX1 is primarily expressed in epithelial cells, vascular smooth muscle, and the colon. It forms a multi-subunit complex with regulatory proteins like NOXO1. NOXA1. and Rac1. enabling controlled ROS production. Dysregulation of NOX1 has been linked to pathologies such as cancer, hypertension, and gastrointestinal disorders, making it a target for therapeutic research.
NOX1 antibodies are widely used to investigate its expression, localization, and function in physiological and disease contexts. These antibodies are typically validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Polyclonal antibodies offer broad epitope recognition, while monoclonal antibodies provide higher specificity. Researchers rely on NOX1 antibodies to explore its role in oxidative stress-related mechanisms, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis. Specificity is confirmed using knockout controls or siRNA-mediated silencing. Due to interspecies homology, many antibodies cross-react with NOX1 in humans, mice, and rats. As NOX1 gains attention in cancer biology (e.g., colorectal cancer) and vascular diseases, its antibodies remain essential for elucidating ROS-mediated pathways and evaluating potential inhibitors.
×