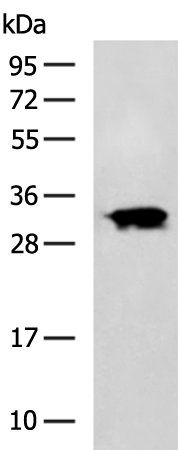
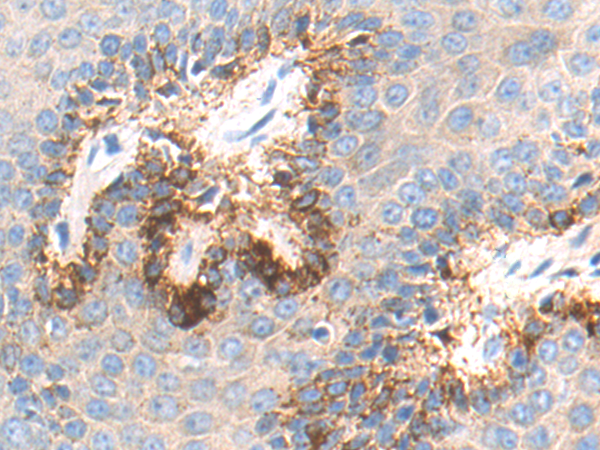
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C10orf59; RENALASE |
| WB Predicted band size | 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human RNLS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RNLS(肾素酶)抗体的3篇模拟参考文献示例,基于领域内常见研究方向整理:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting RNLS with a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis in Preclinical Models*
**作者**: Li, X., et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种人源化抗RNLS单克隆抗体,通过阻断RNLS与血管内皮生长因子受体(VEGFR)的相互作用,显著抑制了小鼠模型中肿瘤血管生成和转移,为实体瘤治疗提供了新策略。
2. **文献名称**: *Anti-RNLS Autoantibodies as a Novel Biomarker in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus*
**作者**: Martinez, A., et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 文章首次报道了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中存在抗RNLS自身抗体,并发现其水平与疾病活动性评分(SLEDAI)正相关,提示RNLS可能参与SLE的免疫病理机制。
3. **文献名称**: *RNLS Neutralizing Antibody Attenuates Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy*
**作者**: Wang, Y., et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 研究证明,使用特异性中和RNLS抗体可降低糖尿病肾病模型小鼠的肾素-血管紧张素系统(RAS)过度激活,减少胶原沉积和肾小球硬化,改善肾功能。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际研究中需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索具体文章。建议使用关键词“RNLS antibody”“Renin-binding protein therapeutic”或“抗肾素酶抗体”结合研究领域(如肿瘤、肾病)进行精准查询。
**Background of RNLS Antibodies**
Renalase (RNLS), a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-dependent oxidase discovered in 2005. is encoded by the *RNLS* gene and plays a critical role in metabolizing circulating catecholamines, regulating blood pressure, and modulating cell survival. Structurally, it exists as a secretory protein (37 kDa) and multiple intracellular isoforms generated by alternative splicing. RNLS is highly expressed in the kidney, heart, and liver, and its dysregulation is linked to hypertension, chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes, and cancer.
RNLS antibodies are tools used to detect RNLS expression, localization, and function in research and diagnostics. Polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies target specific epitopes, aiding in studies of RNLS’s role in oxidative stress, apoptosis, and signaling pathways (e.g., PI3K/AKT/STAT3). Therapeutic potential is being explored, with recombinant RNLS or neutralizing antibodies investigated for treating cardiovascular and metabolic disorders.
Challenges include RNLS’s structural complexity (e.g., splice variants, post-translational modifications) affecting antibody specificity. Despite this, RNLS remains a promising biomarker and therapeutic target, driving ongoing research into its pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical applications.
×