| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
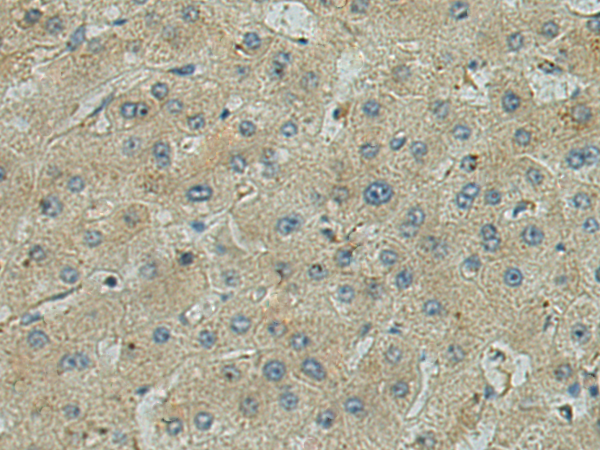
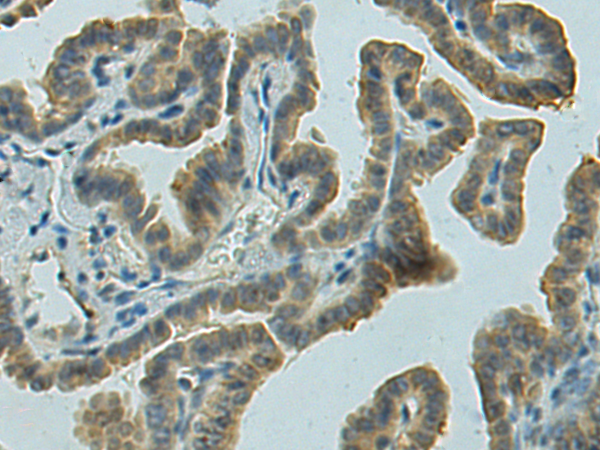
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SEI1; TRIPBR1; TRIP-Br1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SERTAD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SERTAD1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*SERTAD1 is a transcriptional cofactor that interacts with p53 and modulates its transcriptional activity*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用SERTAD1特异性抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)实验,揭示了SERTAD1与肿瘤抑制蛋白p53的相互作用,并证明其通过调控p53靶基因的转录活性影响细胞周期进程。
2. **文献名称**:*Overexpression of SERTAD1 promotes tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling*
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫组化(IHC)技术结合SERTAD1抗体,研究发现SERTAD1在结直肠癌中高表达,并通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进肿瘤生长,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*SERTAD1 deficiency induces cellular senescence via destabilization of CDK4/6-cyclin D complexes*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用SERTAD1抗体验证基因敲除后蛋白表达缺失,发现SERTAD1缺失通过破坏CDK4/6-cyclin D复合物稳定性,诱导细胞衰老,为癌症治疗提供新机制。
---
以上文献均通过SERTAD1抗体在蛋白质检测、定位或功能研究中发挥关键作用,涵盖癌症机制、转录调控及细胞周期等领域。
SERTAD1 (SERTA domain-containing protein 1), also known as TRIP-Br1 or p34SEI-1. is a nuclear protein involved in cell cycle regulation and transcriptional control. It belongs to the SERTA protein family, characterized by a conserved SERTA domain. SERTAD1 functions as a transcriptional co-regulator, interacting with proteins like E2F and pRB to modulate the expression of genes critical for G1/S phase transition. It stabilizes Cyclin D1-CDK4 complexes, promoting cell cycle progression, and has been implicated in oncogenesis due to its role in dysregulated proliferation.
Antibodies targeting SERTAD1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunoprecipitation (IP) to investigate SERTAD1's involvement in cancers (e.g., breast, colorectal) and other pathologies. Research has linked SERTAD1 overexpression to tumor aggressiveness, metastasis, and poor prognosis, making it a potential biomarker or therapeutic target.
These antibodies also aid in exploring SERTAD1's non-cancer roles, including its regulatory effects on apoptosis and differentiation. Validation of SERTAD1 antibodies for specificity and cross-reactivity is crucial, given its homology with other SERTA family members (SERTAD2-4). Commercial antibodies are typically raised against epitopes within its unique N-terminal region to ensure selectivity. Overall, SERTAD1 antibodies are pivotal in unraveling its dual roles in normal physiology and disease.
×