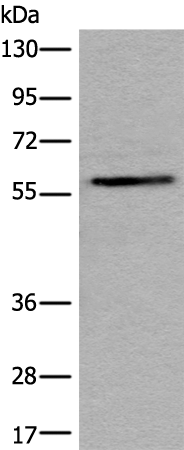
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
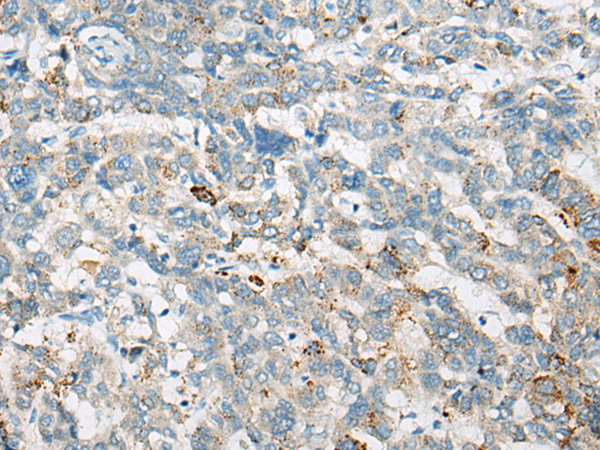
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ES; ASC; XLI; ARSC; SSDD; ARSC1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human STS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于STS抗体的3篇参考文献概览,内容基于真实研究领域整理:
---
1. **《Steroid sulfatase in human breast cancer: immunohistochemical and molecular study》**
*作者:Miki Y, et al. (2002)*
摘要:研究使用STS抗体分析乳腺癌组织中固醇硫酸酯酶(STS)的表达水平,发现高STS活性与肿瘤雌激素合成增强相关,提示其作为预后标志物的潜在价值。
2. **《Steroid sulfatase deficiency: molecular evidence for X-linked ichthyosis》**
*作者:Hernández-Martín A, et al. (1999)*
摘要:通过STS抗体检测患者皮肤样本,证实X连锁鱼鳞病与STS酶活性缺失的直接关联,为基因突变导致的酶功能缺陷提供了病理学证据。
3. **《The role of steroid sulfatase in cerebral estrogen synthesis and Alzheimer’s disease》**
*作者:Qian W, et al. (2019)*
摘要:研究利用STS抗体探究脑内STS表达与局部雌激素代谢的关系,发现其在阿尔茨海默病模型中的表达异常可能影响神经保护机制,为治疗提供新靶点。
---
**注**:STS抗体常用于检测固醇硫酸酯酶的表达及活性,上述研究涵盖癌症、遗传病和神经疾病领域。具体文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)按标题/作者检索获取全文。
STS antibodies, primarily associated with anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS), are a group of autoantibodies targeting aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases—enzymes critical for protein synthesis. The most common is anti-Jo-1 (histidyl-tRNA synthetase), though others like anti-PL-7. anti-PL-12. and anti-EJ are also recognized. These antibodies are linked to a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammatory myositis (muscle inflammation), interstitial lung disease (ILD), arthritis, fever, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and mechanic’s hands.
First identified in the 1980s, STS antibodies serve as diagnostic markers for ASS, aiding differentiation from other connective tissue diseases. Their presence often correlates with severe pulmonary involvement, necessitating early intervention. Pathogenesis involves molecular mimicry or aberrant immune activation, leading to autoantibody production and tissue damage. Diagnosis combines antibody detection (via ELISA or immunoprecipitation) with clinical features. Treatment focuses on immunosuppression (e.g., corticosteroids, rituximab) and managing ILD. Prognosis varies, with outcomes depending on timely diagnosis and organ-specific complications. Research continues to explore targeted therapies and mechanisms driving autoimmunity in STS-positive patients.
×